So I was listening to a radio presenter this morning. A very interesting subject of discussion was raised and this had to do with the question relating to why some individuals do have discoloration of hairs especially young adults at their early 20s and above. For sure, it is something to find out. Could it be a normal thing in humans or caused by something else.
I got curious because I have observed this to be more common and among young and middle aged people. Infact, I have a close friend who started seeing grey hairs at the very young age of about 19years. Back then, I would think it is just his nature and probably he cannot do anything about it since it is supposedly natural. Well, my guess maybe right or wrong then, today, as you read this article, you will understand.
 Elderly people with grey hairs
Elderly people with grey hairs
Gone are the days when it is believed that, the presence of grey hair is an indication of wisdom and maturity. To some extent, this is true and on the other hand, it is also a false assumption. Being intelligent, wise and smart is not a direct function of presence of gray hair or its absence. Today, there are older people who act like kids and there are also young people who behave and act so matured that you begin to wonder if truly they are young.
Without further adieu, let's get on with the scientific basis behind our subject of discussion. To have a better understanding of our topic of today, the best way is to have a good understanding of hair, how is it that our hairs differ in colour and what gives them those characteristic colours. Let's take a quick delve into an overview of human hair.
It is generally proven fact that the intensity or concentration of a pigment associated with humans determines our colour and also the degree of colour expression in humans. This pigment is known as the melanin. They are mainly responsible for providing the skin, hairs and our eyes their colour pigment. In essence the colour of our hairs, skin and eyes is determined by the concentration of melanin.
Melanin is produced by cells in the body known as melanocytes. They produce basically two forms of melanin pigment that are found in the skin. These forms include those predominant in the skin - pheomelanin and eumelanin. Another form of melanin is also found in the brain and from its name, it's obvious - neuromelanin. So in total, there are three basic forms of melanin.
The varying concentration of this forms of melanin determines the skin colour of individuals and it also goes a long way to confer some types of colouration to some parts of our body. Besides the conferring colour to the human body, they also perform a very important function of protecting us against the photo radiation from sun.
This photoprotection is offered by the keratinocytes which contains abundant melanin in concentration. Without melanin in abundance, the effects of sun UV radiation could cause severe burns and if not handled, it lead to skin cancer. Black skinned individuals have melanin in high concentration compare to someone that is light skinned.
It is reasonable at this point to ask, what then happened to individuals who are white, dark in colour, and as well as the albinos (those who lack melanin in its entirety). The Africans are regarded as black because of their darkened skinned colour while the West, Asians, Europeans etc. are referred to as the whites because of their light skinned colour. Albinism is an inherited disease condition that results to lack of melanin production.
The major driving factor of melanin production is the presence or intensity of sunlight's ultraviolet radiation onto the skin exposed to it. The higher the intensity, the more melanin are produced. The body's exposure to sunlight UV radiation causes what is known as Tanning (darkening of the body's part that is exposed to sunlight).
Albinism predisposes individuals to skin cancer because they, melanin which helps absorb the UV radiation of the sun is either in low amount or totally absent. The greater the concentration of melanin, the greater its ability to absorb UV radiation and vice versa.
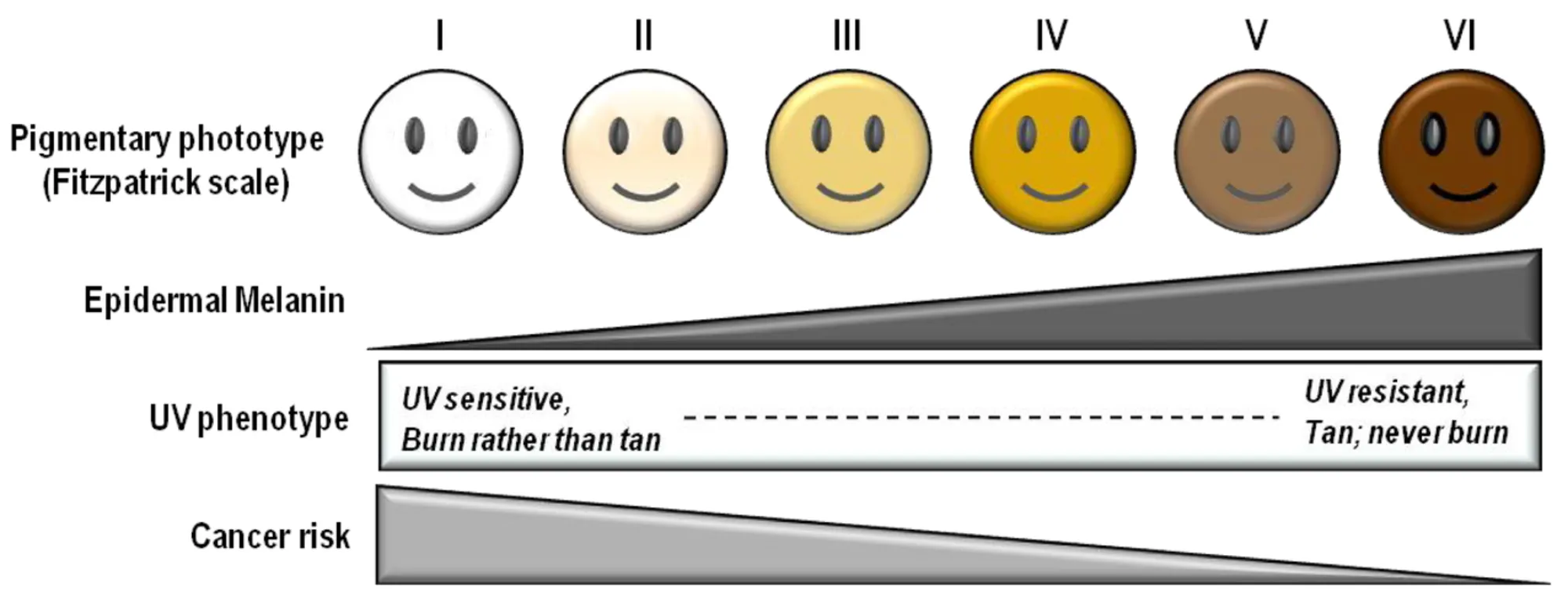 Influence of pigmentation on skin cancer
Influence of pigmentation on skin cancer
UV radiation have damaging effects because of their ability to alter DNA sequences, and any alterations of any form in the genetic sequence, could lead to cancer.
Impact of bleaching creams
People that bleach actually reduce the concentration of this melanin in their skin and by so doing, the skin gradually changes from dark and become fair. The active ingredient in most bleaching cream is the steroid hydroquinone and it acts by disruption the keratin layer in the epidermis. This disruption causes the reduction or inhibition in the production of melanin in the individual hence the light skin expression.
Bleaching creams also contains some heavy metals like mercury and as they are deposited continuously on the skin, by dermal absorption, they are deposited in the kidney. Overtime, they cause what is known as nephrotic syndrome. This can progress to kidney failure.
The diversity in skin complexions
Africans tend to have darker skin complexion not just because of the abundance of melanin production, but also, because of climatic condition. The hot environment caused by the sun's intensity accelerates the production of melanin by melanocytes in the keratin layer of the skin's epidermis. The more they are exposed to the sun, the more melanin are produced to cushion the UV radiation effects. In other words, melanin is protective in nature.
This is why you would observe that, some parts of the body like the thighs and laps which are not exposed to sun, tend to be lighter in complexion as when compared to your hands, face and legs which will look darker because they are mostly in direct contact with the sun.
However, without the impact of the sun's UV radiation, people still vary in skin colour, likewise some parts of our body, why is that?. Read on, you will find out.
As we earlier established, the varying concentration in the forms of melanin, confers the different skins colours in humans. This variation is shared and exists between eumelanin and pheomelanin. These two forms of melanin, in conjunction with their producing cells- the melanocytes, are responsible for different colour of our body parts.
Ever wondered why some parts of the body are always coloured red. For example, the nipple area of the breast, the vagina, glans penis and most interestingly the lips. Ignorantly before now, some of us (me inclusive) used to think that these parts of body are red because they have abundant supply of blood.
To some extent, the above can be argued to be true with some substantial facts because, these areas can look very pale and white in anaemic (low blood level) conditions and they can serve as a very useful diagnostic tool in having an idea of a patient's blood level but the real fact behind the colour of those areas of the body is because of increased pheomelanin concentration.
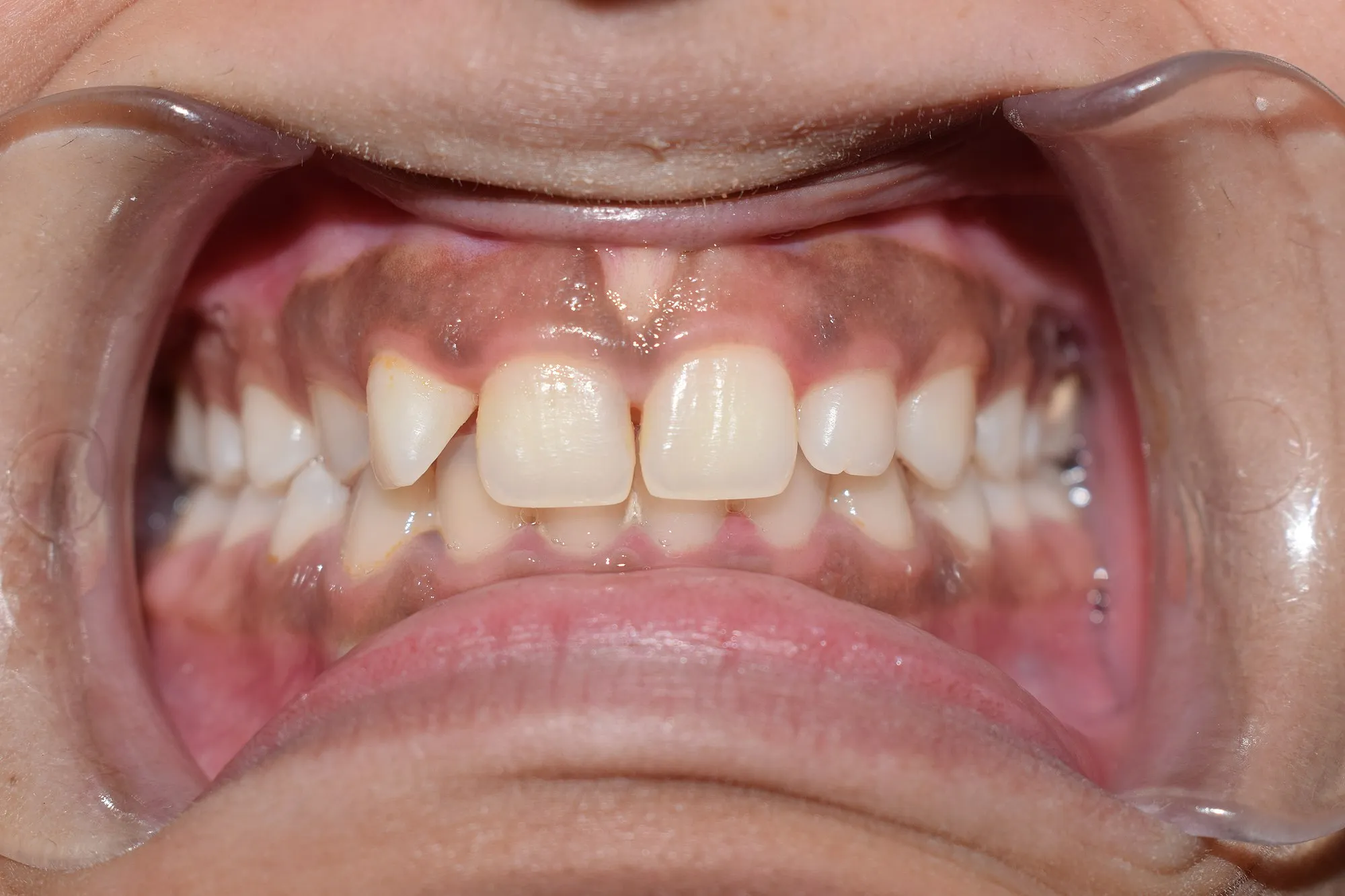 Melanin gingival hyperpigmentation
Melanin gingival hyperpigmentation
Regardless, there are in some conditions where they look very darkened and this is usually due to hyperpigmentation (excessive deposition of melanin in such areas). This hyperpigmentation can occur in the lips, or even the teeth gum (gingiva).
Pheomelanin which is a form of melanin produced by the body melanocytes is yellow-red in colour, and it is primarily responsible for the pinkish red colour of the lips, tongue, nipples etc. On the other hand, eumelanin which is black-brown in colour confers the black colours to some parts of the body like the hair (specifically in those with black hair). This brings us closer to our topic question.
Why we have variety of human hair colours
Just like we earlier explained, done parts of the body take their colours as a result of either eumelanin or pheomelanin concentration and abundance. The determining factor is the ratio of their presence or absence. When one is present in abundance, it overshadows the other and vice versa. This principle also applies to the human hairs.
Probably you have been wondering why someone who is fair in complexion turns out to have a very thick dark hair. Why is this so? The reason is simple, genes control the expression of a lot of characteristics in humans. Your gene could down-regulate less production of melanin in your skin thus making you fair in complexion. This might not be the same with your hair.
The genes for hair growth processes might be programmed to be upregulated to produce more melanin, thus making your hair darker in colour. In essence, it all depends on your genetic predisposition. What you inherit, determines your physically expressed traits.
The reason for hair colour differences among individuals is simply because of the difference in ratio of concentration between the two forms of melanin - eumelanin and pheomelanin. In individuals with very dark black hairs, eumelanin is high concentration. This however does not make them black skinned. In those with brown hairs, it means that eumelanin is in moderate amount while lastly, those with blonde hair, have very little of eumelanin. You could be fair and still have black hairs.
Similarly, in individuals with with red or pinkish hairs, it means that the melanocytes are producing more pheomelanin than eumelanin, even though the latter is still present but in minute concentration.
Why hair change colour at old age
It is a known fact all cells at one time will get old and undergo apoptosis (natural cell death) and this is facilitated by the enzyme known as caspases. They are triggered to initiate cell death once the cells have reached the end of their natural life span. The hair follicles are responsible for producing melanocytes.
As we age, their functions also reduce and overtime, they totally stop the production of melanocytes. Recall that melanocytes are responsible for producing melanin, a pigment that gives the hair its colour. The decline in the production of melanocytes by the hair follicles is usually noticeable with the hair gradually becoming lighter gray in colour until it turns completely white, meaning, there has been an abrupt stop in melanin production.
In summary, human hair turn completely white or looses it colour because of the stop in melanin production by the melanocytes, which in turn is a function of the state of activity or functionality of the the hair follicles. All things being equal, the human hair is supposed to turn white once the hair follicles have stopped melanocytes production, why then do young people have gray or white hairs? Let's quickly answer the ultimate question we have all being waiting for.
Reasons for gray or white hair in young individuals
Basically, if all things be equal, physically expressed characteristics are control by the genes we inherit. Some individuals start having gray or white hairs at a very young age of 30 or less, while in some, it occurs later at grey old age (60years and above). This is a clear evidence of aging in humans, so we can say it is normal and physiological.
In some individuals, these discolouration can start at age below 30, now this is sure not physiological and most times could be as a result of an abnormality. Research has shown that, there a myriads of reasons for hair discolouration at early age. Two of this, is a disease conditions called are called Vitiligo and poliosis. Let's be careful not to confuse vitiligo and poliosis even though they both share similar appearance. They are not the same.
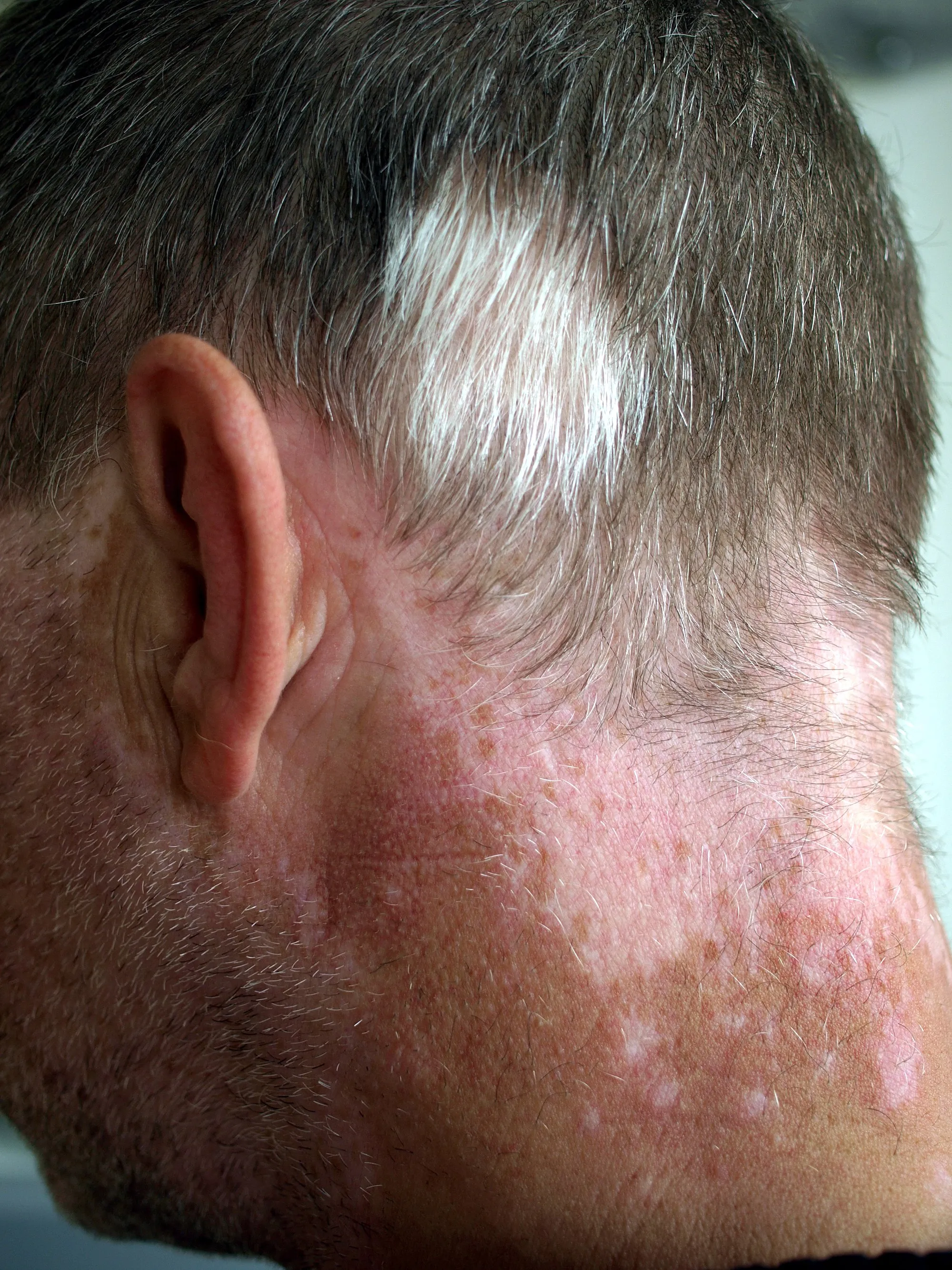 Depigmentation of skin and hair in 48-year-old man caused by vitiligo and poliosis
Depigmentation of skin and hair in 48-year-old man caused by vitiligo and poliosis
Vitiligo is basically a skin conditions that causes the skin to loose its pigmentation and as a result, it turns while in colour. It usually appears as a white patch on the skin and can occur at any part of the body. The most common cause of vitiligo is autoimmune disease (a disease condition that causes your body immune cells to attack its own cells). When the melanocytes are attacked and damaged, they either are rendered less active and unable to produce enough melanin pigment and at some point they will not produce at all, hence the discoloration seen on the body.
Other disease condition that leads to vitiligo include hyperthyroidism (over active thyroid gland). Just for emphasis, the thyroid gland plays a big role in the production of melanin because it produces the tyrosine needed for the synthesis of melanin by melanocytes. So deficiency of tyrosine can also cause a individual to have early gray hair.
Even cancer of the melanocytes (melanoma) can also be a contributing factor to hair and skin depigmentation. Unfortunately, this disease condition is not curable, the speed of the disease progression can be delayed but not stopped. Most medications only end up restoring the colour of the skin. Treatment is usually more effective at the early onset of the disease.
Poliosis on the other hand mostly affects the hair directly. It still has similar etiology as vitiligo, which is lack of melanin. They usually appear as a patch of discoloured hairs and can occur at any part of the body. Sometimes, they could be genetically inherited thus, not necessarily a problem.
Another factor that could also cause discolouration of hairs is depletion in vitamin B12. This vitamin plays a major role in the formation of hair and its colour. When they are deficient in individuals, they can cause the hair to loose its pigmentation. Even deficiency in vitamin D and biotin (B7) can also contribute to loss of hair pigmentation.
Furthermore, stress has also shown to contribute to quick hair loss in individuals. Oxidative stress is a major factors that has been implicated in faster ageing in people. The simple science behind this, is the fact that, oxidative stress is accompanied with the production of excess radicals (reactive oxygen and nitrogen species) that cause oxidative damage to healthy cells in the body.
These damage can affect the hair follicles thus, leading to issues with melanin formation. One of the agents that contributes to oxidative stress is smoking. People frequently, are at higher risk of increasing the level of oxidants in their body.
Permanent hair colors often contain ammonia (or chemicals similar to it) and peroxide. The ammonia breaks through your hair shaft, and the peroxide neutralizes (or bleaches out) the natural pigment in your hair, stripping away color. This process of relaxing the hair cuticles to reach the cortex of your hair and bleach out its natural pigment is, essentially, hair damage.
Chemicals used in dyeing hairs contains chemical that could as well damage the hair. Most of them contain hydrogen peroxide which is an oxidant. Dyeing of hair is now common among the youths and most ignorantly fail to understand the repercussions their actions have on the hair.
It is even preferable to dye a natural white hair at old age than dye a natural hair at young age. Better still, leave the natural hair the way it is. The consequences of our actions sometimes are never immediate, they tend to manifest at the long run.
Report has shown that graying of hair associated with stress are mostly reversible. What this simply means is that, by changing your life style and eating healthy, the hair follicles can return to normal functional state and produce melanin pigments.
In conclusion, it is better to keep the hair safe by taking care of it. Avoid and reduce the use of dyes. Some chemicals used in the production of these dyes are carcinogenic in nature, as much as possible, reduce or totally stop the usage. Dyeing hairs and bleaching the skin puts you at greater risk of sunburn because, these two procedures reduce the concentration of melanin in the body and by so doing, they leave the skin at the mercy of the sun's UV radiation.
Till I come your way, please keep that lovely hair healthy!
References •Human Hair and the Impact of Cosmetic Procedures: A Review on Cleansing and Shape-Modulating Cosmetics •Premature Graying of Hair: Review with Updates •Overview - Vitiligo •Minimal change disease caused by exposure to mercury-containing skin lightening cream: a report of 4 cases •Inorganic mercury poisoning associated with skin-lightening cosmetic products •What to know about melanin •SOS: Why Is My Hair Turning White? •Changes in hair color •Human Hair Graying is Naturally Reversible and Linked to Stress
Return from Are all white hairs age dependent or caused by a disease? Let's do a deep research to cyprianj's Web3 Blog


