During my leave early this year, I got talking with one of my very good friend's mother. In the course of our discussion, she narrated a story that actually struck me. How people in her time used a plant as a means to either get back at their offenders or punishment for wrong doings.
The story got more interesting when she mentioned the name of the plant- The Devil's beans (as popularly called in Nigeria). As a researcher, I was very inquisitive to find out what really is behind the name this plant was tagged. This got me thinking seriously. The content of this article are simply some findings I made online about the Said devil's beans. Enjoy!
Let's start this discussion quickly by diving into the scientific nomenclature of the said devil's beans. As you read along this expository, it will review a lot of intricate details about this plant and why it is referred to as devil's beans, especially in west Africa, Nigeria.
Brief Nomenclature
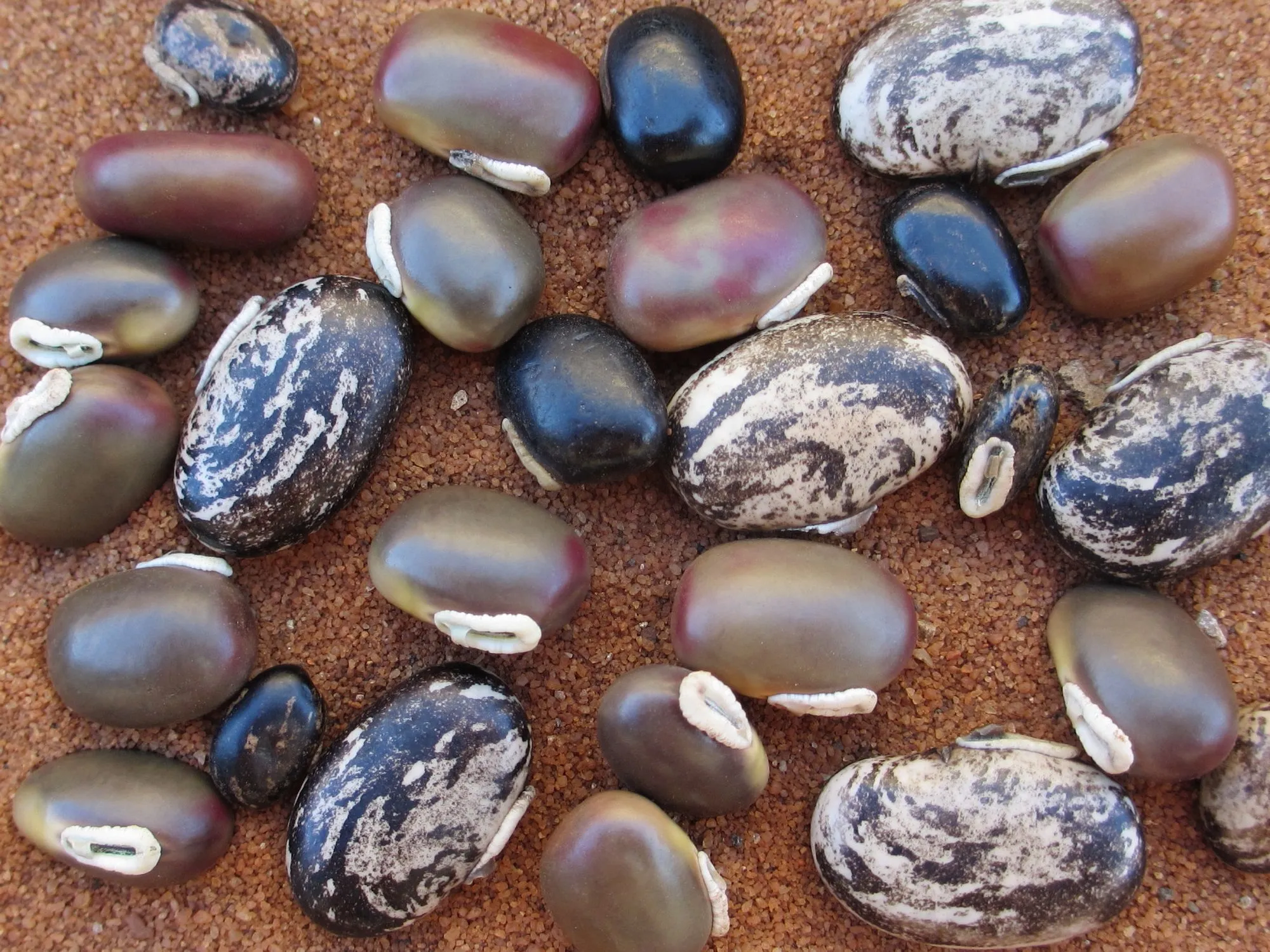
Mucuna pruriens (MP) belongs to the family of Leguminosae, by implication, it is a legume and to make it more simplified, it is a beans. It has up to 100 species. This simply gives you an idea of the fact is really has a wide family. It is also known as Fabaceae.
MP is found in the woodlands of tropical areas especially in Africa, Asia, India and the Caribbean (ejeguo et Al., 2019). It is known with so many names such as devil's beans (Nigeria), velvet beans (English), Pois a gratter (Europe), Ci mao li dou (Asia) etc.
I am sure you are really curious to know why Nigerians refer to it as the devil's beans, in due time we will sure find out.
Narrowing the names more to Nigerian tribes, the Igbos call it Agbara while Yoruba's call it Werepe.
Recently, this plant is gaining the attention of the science community, especially the pharmaceutical industry because of the presence of some very useful phytochemicals with huge potency of being used to manage neurological conditions like Parkinson's disease.
In the course of discussion, we will dwell more on these phytochemicals that makes MP a very useful and beneficial plants.
Why the name devil's beans
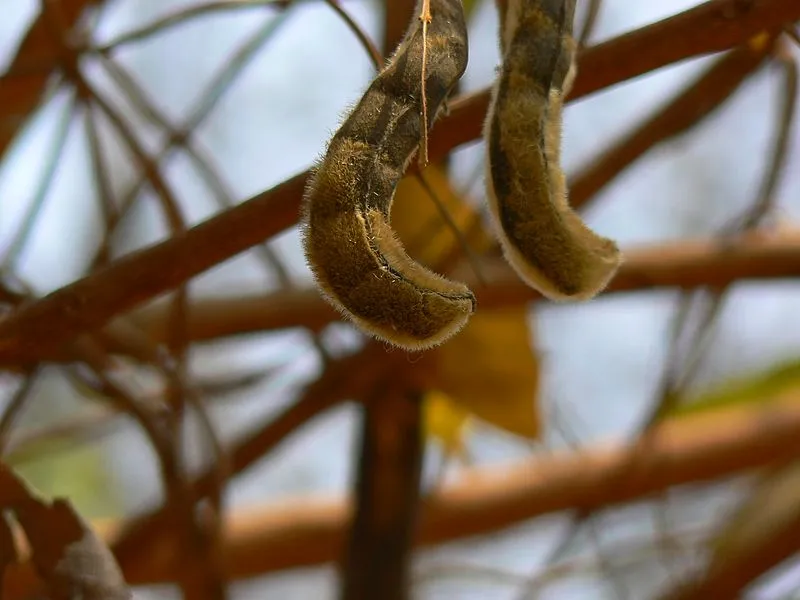
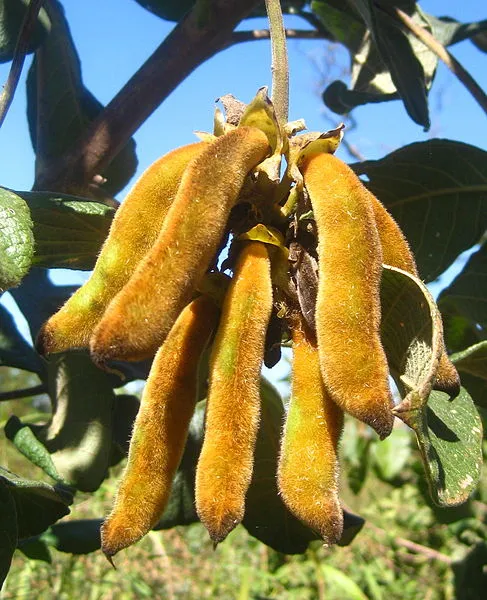
With respect to Nigeria, MP is one of the most dreaded beans in the farm because of its spiky stinging hairs that causes serious irritation on contact skin and eyes when they dislodge from their pod.
A sting from this plant's hair can actually make you go 'gaga'. The itching continues for a very long time if post exposure measures are not taken to surpress the itch.
From our discussion, she narrated how people used the hairs of this plants to perpetrate wickedness to their fellow humans by intentionally spraying the hairs of this plants on clothes of their victims or in their bathing water. The rest is history.
This was actually the logic behind the name - devil's beans. Even in the bush, hairs from dried pods of the beans is not dreaded. While in the farm, you don't want to go close to the pods.
Why the itch?
Now we have gotten story, what then is the science behind the reaction. I always love finding facts rather than speculations or stories that do not have any reasonable scientific explanations. If it is not proven, it is not a fact and not worth spreading.
The hairs on the plant cause itchiness and this is as a result of the presence of Mucunain (a proteolytic enzyme - an enzyme that has the ability to degrade or break down proteins) and Serotonin (a hormone that is strongly associated with mood stabilization, feeling of wellness and happiness.
The Mucunain and serotonin the major content that induces the severe itching on the victim and as they scratch the affected area, its spreads to other area thus causing more itching.
Because of the way it induces the scratching and how vigorous and uncontrollably the victim scratches, in Mozambique, it is referred to as 'Mad beans'
The pharmacological potency
According to research, dry MP has been found to contain a relatively high level of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA), a compound that has a lot of function and one of which is that, it serves as a precursor for most neurological transmitters like adrenaline, noradrenaline and dopamine. These group of neurotransmitters are called catecholamines.
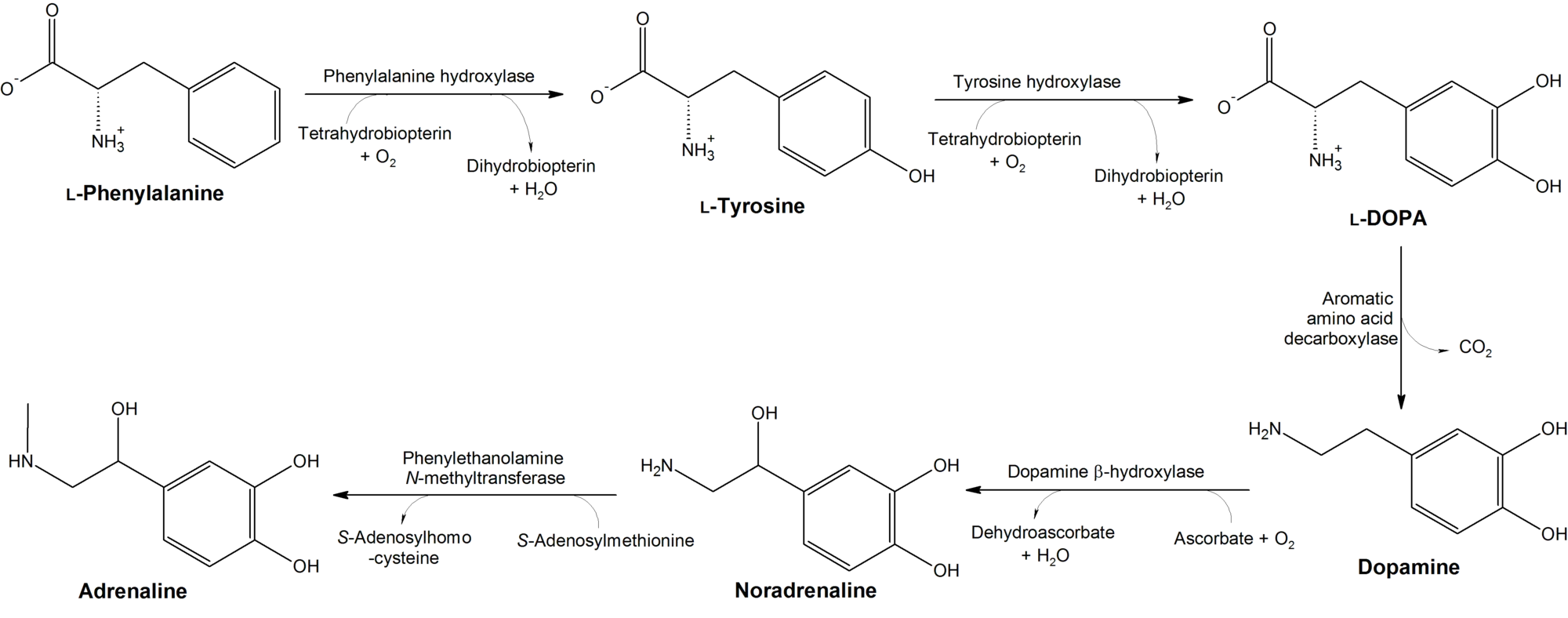 Biosynthesis pathway for catecholamines from L-DOPA
Biosynthesis pathway for catecholamines from L-DOPA
One of the easier way of extracting this L-DOPA from MP is by boiling boiling the seed and later soaking it for up to 48hours. This will yield about 80% of the compound from the seed.
Since it contains high concentration of the toxic compound L-DOPA which is a precursor for catecholamines, it has been since used in the treatment of several neurological conditions like Parkinson's disease (a chronic and progressive movement disorder with symptoms that continue and worsen over time, with a hallmark sign of clumps of theprotein alpha-synuclein — called Lewy bodies).
It is also used in the treatment of other disease conditions like reproductive disorder, menstrual issues,fever, constipation and a host of other problems. Commercially, MP aka velvet beans is the source of L-DOPA.
MP role in reproduction
Talking about the reproductive issues, MP is one of the most recommended reproductive tonic for both men and women in Nigeria, this is found in the report of Ejeguo et al., 2019.
It has been indicated in boosting healthy sperm and ova production in both males and females respectively.
In history, MP has been used as a very effective aphrodisiac and till date, it is still being used to boost libido because it of its dopamine content.
Dopamine has huge role to play in reproduction by speeding up most importantly ovarian development and in healthy sperm formation through improvement in testosterone level.
According to the work of Yera (2005) reported in Amira, (2014), a typical dose for a man is 15g of ground seeds mixed with cow’s milk.
Since MP has the ability to boost and increase testosterone as well as growth hormone production, it makes common sense for it to be able to increase muscle mass, besides it is a legume. This is one the reasons why it is desirable for men that are mostly engaged in sporting activities.
Interestingly, all parts of this plant is highly beneficial to humans. Besides the pharmaceutical potencies, it is also an edible legume thus a source of protein.
The minor negative aspect of this plant, is the stingy hairs that covers the entire body of its dried pod.
Harvesting this beans during rainy season is safer than harvesting them during dry season. The idea behind this is that, during rainy season, the hairs are wet and cannot easily sting, compared to when it is dry. The pods of the matured ones usually look brownish in colour. The E
MP power of longevity
Promotion of longevity is also another implicated potency of MP. The research by Tripathi and Updhyay, 2001 reported in Lucia Raffaella, 2012 showed that the methanolic extract of the seed of MP contains high concentration of antioxidants thus they have the ability to increase the concentration of endogenous antioxidants like Superoxide Dismutase in the body.
Endogenous antioxidants are substances that help the body naturally to boost the immune system by reducing the level of oxidants. Oxidants are reactive Oxygen and nitrogen species that have the ability to cause damage and degradation of tissues.
Naturally, humans tend to age faster if there is an increase in the concentration of oxidants and decreased level of antioxidants.
In order to augment the efforts of the body's defense system, taking foods (e.g Fish etc) and fruits (orange etc) rich in exogenous/endogenous antioxidants like Vitamin A, C, E, Glutathione, will help boost and shift the equilibrium in favour of the antioxidants.
Imbalance or disproportionate level in the oxidants/antioxidants ratio in favour of oxidants is what causes diseases in humans. One reason why we are always encouraged to eat and take enough fruits as part of our routine diet. So in essence, a shift in the balance between these two can either be favourable or otherwise.
MP is to an extent edible in some countries even though it is not a regular kind of food. They are eaten in Mozambique most especially in cases of food scarcity. Though processing the legume can be very tedious so as to remove the high concentration of the toxins and of which is L-DOPA which is in high concentration.
"Velvet beans can be used as a human food but require considerable care in their preparation... In many parts of Africa and Asia they are regarded as a famine food. The toxic principle can be removed by boiling and soaking the seeds in several changes of water. Echo Community"
Role of MP in conferring immunity against snake bites
In the course of this research, I got to discover that, MP has the power to confer immunity against snake bites. I am as shocked as you are right now because I wondered, how possible can this be?
As reported in Lucia Raffaella Lampariello (2012), MP is one plant that has been shown to be active against snake venoms. The seeds of this plant have the ability to inhibit the toxins in snake that usually trigger the toxic effects of snake bites.
In Nigeria, Plateau State to be precise, the seed of MP is given orally as a remedy for snake bite by traditional medical practitioners.
It is believed that when you swallow the seed in its intact form, it has the capacity of protecting one against the deleterious effects of snake bite (Guerranti et al., 2001) in Lucia Raffaella Lampariello (2012).
The above claim was later investigated scientifically and was found to be true even though the duration of 1 year was not backed yet with any proof.
The investigation by Guerranti et al., (2008) to verify the claim above showed that the protection against the effect of snake venom was evident within 24hours and then up to even a month when the injection of MP aqueous extract was administered long term.
Further investigation to find out the possible mechanism of action of this plant revealed that MP aqueuous extract contained an immunogenic glycoprotein called gpMuc.
This glycoprotein has the ability of forming a cross reaction and binding to the toxins in the snake venom, thus rendering them inactive Roberto Guerranti et al., 2002, Nnadozie Stanley Hope-Onyekwere et al., 2012 .This simply explains the long term protection potential. It was also discovered that MP aqueuous extract contained protease inhibitors that are strongly active against snake venom, (Roberto Guerranti et al., 2008)
Limiting factor to MP general use as regular food
It is well known that most tropical plants are made up of many phytochemicals constituents that can cause deleterious effects when consumed without proper assessment. Infact, legumes followed by cassava contains more toxic compounds than other crops.
In moderate or small amount, these phytochemicals can prove to be beneficial health wise but upon excessive consumption or non regulated consumption, they cause serious problems.
These phytochemicals include the following: Alkaloids, tannins, L-DOPA, Saponins (aka steroids or terpenoid glycosides). Glycosides are also natural detergents. The phytochemical contents of plants are the major contents that confer the astringent and bitter taste you experience when you take them raw.
These plants also have high potency to cause haemolysis (lysing or destruction of red blood cells). This is why it is not and never advisable to take herbs or traditional preparations without dosage.
Always remember, only the dose makes anything safe or a poison. In essence, all presumed drugs are poison, what makes it safe is the dose. Loading non standardized herbal mixture (a herbal whose active substance concentration is not known) can be very dangerous.
Findings from the work of Amira, (2014) suggests that MP if well processed is beneficial and healthy for consumption.
The study compared and evaluated the anti nutritional factors of MP and Sphenostylis Stenocarpa aka African Yam beans. The study found that Saponins were also in concentration good enough to be beneficial to humans.
Saponins are generally known to lower cholesterol level, inhibit cancer cells and as well boost energy. There might be limiting factors to MP Wide consumption, but facts so far have shown that it is really a good plant worth exploring more. All that is required is good preparation for its consumption and right dosage if for pharmaceutical use.
In conclusion...
Mucuna pruriens hairs causes serious and intense uncontrollable itching, hence the name devil's beans (given to it by Nigerians) or mad beans (As called by Mozambicans) because of two major chemicals namely - serotonin and mucunain and it has so far been established as a herbal drug that is used for the management of male infertility, nervous disorders (Parkinson), and also as an aphrodisiac. It contains high concentration of L-DOPA. This goes beyond rumours but rather has been proved overtime with empirical scientific evidences and facts.
The health benefits of this plant outweighs its negative aspect thus, can be of great benefits to humans when added in moderate amount in diets. In health and pharmaceutical industry, this plant will be of great benefit because of its vital constituents.
There are more health benefits associated with MP which I found in the course of the research, some of the journals are in the reference section of this article for your perusal.
Indeed, Mucuna pruriens has a lot to offer, judging and disregarding the plant just because of its outer look or appearance would be the wrongest thing to do. Never judge a book by its cover. You never can tell what you may find!
Until I come your way again 😉
Thanks for reading.
References
•PUBMED; The Magic Velvet Bean of Mucuna pruriens - Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine •PUBMED; Proteins from Mucuna pruriens and enzymes from Echis carinatus venom: characterization and cross-reactions •PUBMED; Proteomic analysis of the pathophysiological process involved in the antisnake venom effect of Mucuna pruriens extract •PUBMED; Effects of Mucuna pruriens protease inhibitors on Echis carinatus venom •PUBMED; Alkaloidal constituents of Mucuna pruriens seeds •Chemistry of L-DOPA •Effects of Aqueous Leaf Extract of Velvet Bean (Mucuna Pruriens) on Reproductive Outcome in Adult Female Wistar Rat •Echo Community project - Evaluation of Mucuna pruriens •Evaluation of Raw and Boiled Velvet Bean (Mucuna utilis) as Feed Ingredient for Broiler Chickens •The competitive advantage of velvet beans as an economic agricultural commodity •Comparative Studies on Some Anti-Nutritional Factors in Seeds of Mucuna Pruriens (Velvet Beans) and Sphenostylis Stenocarpa (African Yam Beans) •Effects of different methods of processing velvet beans
Return from Beyond the evil, lies the good: The devil's Beans expository to cyprianj's Web3 Blog