Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role our genes play, its behavior and the environment in which it is domiciled gives us better perception about human disease pattern. It also goes as far as helping us understand and differentiate between the norm and the abnormal. It is imperative for every newborn to undergo some very important screening after birth. These screening have huge clinical significance and their results have guides a lot of decision to be made.
We will briefly and quickly look at some of the genetic test and newborn screening and briefly describe them. We will also explore how they are done in the health facility and also look at their clinical significance. Reading this article will sure give you an hint on what goes on in the pediatric departments of health institutions, the significance of genetic testing and also enlighten you on what you probably do not know.
The crucial role genetic information have played in genetic diseases diagnosis and management
The world has evolved so well that we are now able to apply the information gotten through gene sequencing into diagnosis and treatment of both genetic and non genetic diseases. These set of data are usually called the BIG DATA because they have 5 basic characteristics. In my subsequent article, we will really discus the concept of Big Data and what it is all about, in the mean time, lets focus on our newborns.
Genetic information has really helped us a lot. Information from genes so far has helped and guided us in in the area of appropriate patient care and also in the area of precision medicine (concerned with identifying the particular treatment unique to an individual). Diseases and disorders usually have pattern and understanding them early enough, reduces their rate incidence or rate of occurrence globally.
Early detection they say is better than cure. Detecting a disease condition while it is still relatively early enough will sure offer a better and promising prognostication. Genetic diseases mostly are inherited from parents to offspring during embryogenesis. The inheritance pattern usually vary depending on the nature of the gene for the particular trait in question.
Based on the classically Mendelian inheritance pattern, the genes could either be autosomal dominant or recessive, X-linked dominant or recessive and lastly it could be through mitochondrial inheritance. The rate of genetically inherited diseases have been drastically reduced over the years due to proactive measures taken by government agencies around the world. What if there was no intervention, what would have been the fate of many newborns with potential genetic diseases.
Newborn Screening; an overview
Based on reports, each year, more than 95% of all children born in the United States for example (at least 4 million babies) are tested for a panel of diseases that, when detected and treated early, can significantly reduce the disease severity and possibly even prevention of the disease. Out all the tested babies, About 3,000 newborns test positive for one of these severe disorders.
The five most commonly diagnosed conditions in the United States are hearing loss, primary congenital hypothyroidism, cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and lastly medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
Basically, newborn screening test are done within 48 hours of a child’s birth, a sample of blood is obtained from a “heel stick,”. After collection, it is then analyzed. There are about up to 50 diseases that can be analyzed with the sample collected including phenylketonuria (PKU), sickle cell disease, and hypothyroidism. Just so you know, the blood collected is referred to as “blood spot,”. This blood is tested in the laboratory. There are a host of screening test done on infants (over 50 tests) but for want of time, we will just select a few of them that are very very important and poses great threat to children social and academic life and discus. lets start with Hearing Screening for newborns.
Newborn Hearing Screening
taking United State of America as a case study, all infants and newborns are usually required by law in the US and some other well developed countries for example, to be screened at birth for hearing loss. This approach as I earlier stated above is aimed at drastically reducing hearing loss in children. One of the disadvantage of failing to do this is that, the child could experience delays in speech, language, emotional, and educational development. All this will only amount to more burden on both the government and family of the child.
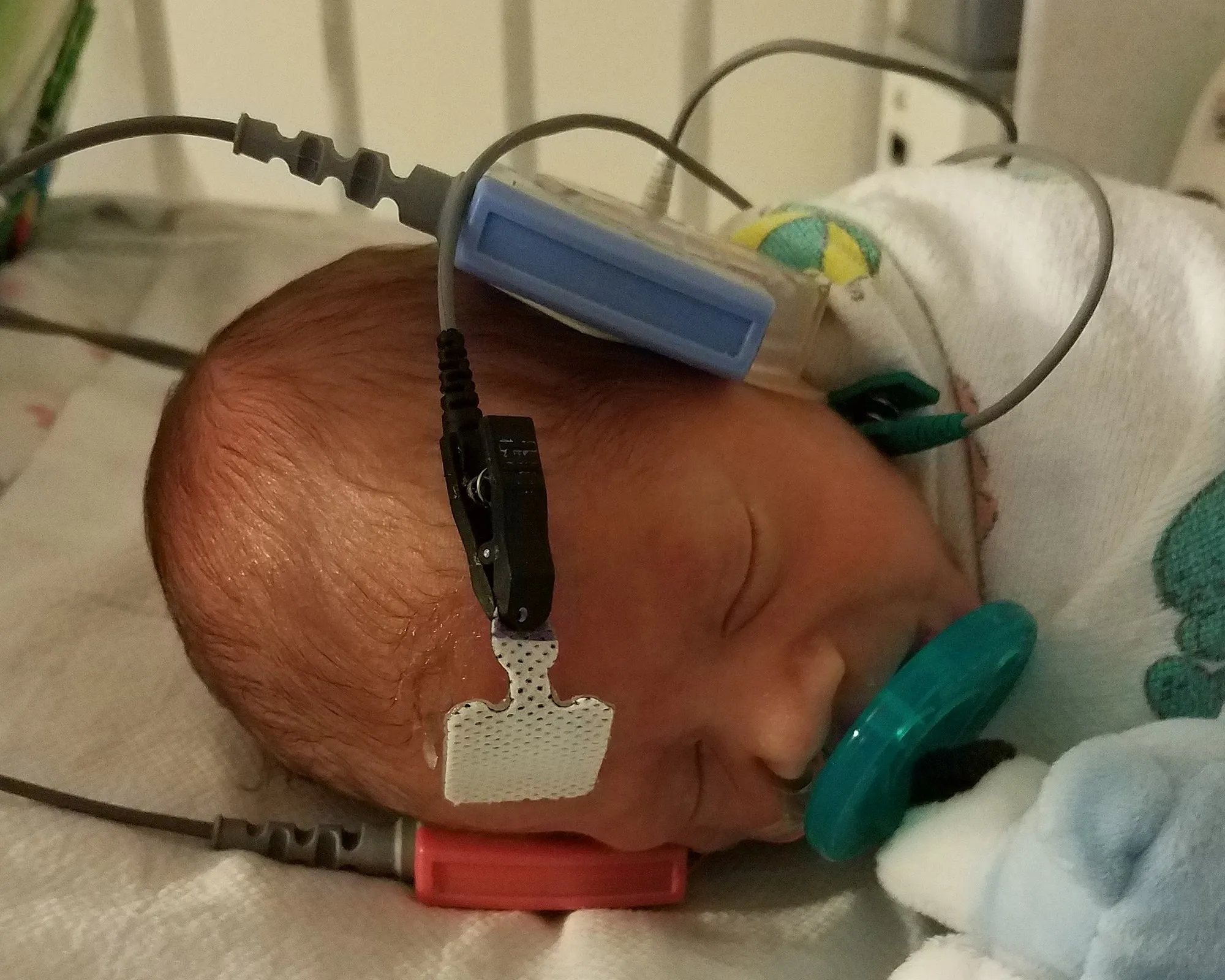 A newborn infant undergoes a hearing screening
A newborn infant undergoes a hearing screening
When it comes to screening for hearing loss, there are two major tests: OAE (otoacoustic emissions) and ABR (auditory brainstem response). A baby may be given one or both of these tests. I will try as much as possible to simplify the procedure.
In the OAE test for example, the procedure is done by inserting a very soft rubber earpiece into the baby’s ear. This is done with the intention of delivering a soft sound. The baby's reaction is measured and recorded with the audiometer which is handy. This test basically measures how well the baby’s inner ear is able to respond sound while in the ABR test, earphones are placed over the baby’s ear canal to deliver sound. This test measures how the brain responds to sounds.
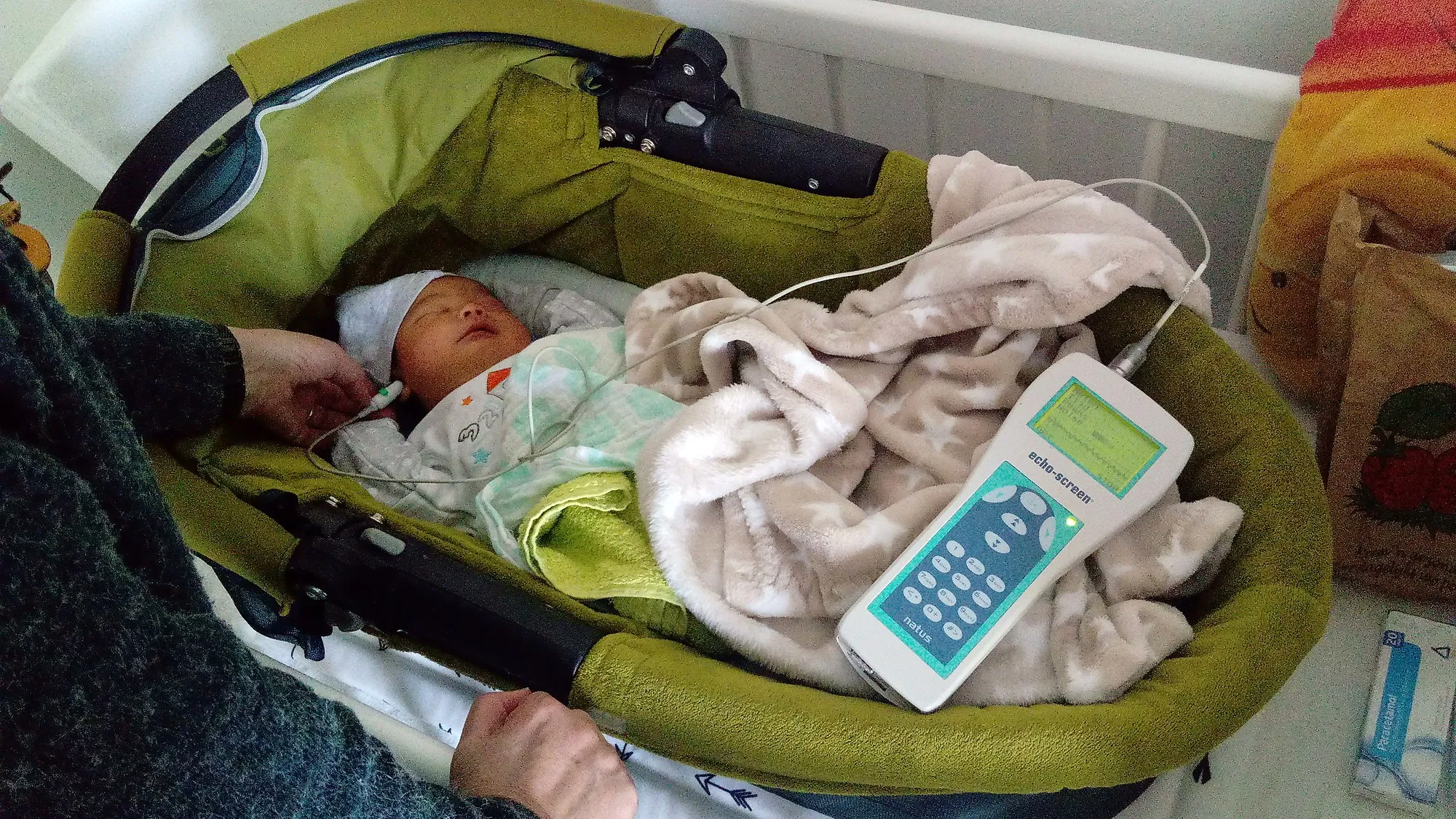

A young infant being screened for possible deafness in the Groninger village of Oude Pekela
It is worth knowing at this point that, this testing is done mostly when the baby is asleep and not aware of the testing. All things being equal, the results are usually available as fast as possible. In situations where the baby passes the screening test, it simply means that the baby’s hearing is within the normal range at the time of the test. Note that in some babies that probably have a family history of either consistent ear infection ,hearing loss or serious illness, the chances that they may later develop hearing loss later is also possible. This is why it is very important that the child’s hearing and speech should be monitored as he or she grows up.
Should the baby not pass the hearing screening test, then it means that the baby would have a second hearing test. Failing the first test does not necessarily mean that the baby has hearing impairment. They are usually subjected to second screening while they are still in the hospital or within two weeks after leaving the hospital.
If the baby does not pass the initial hearing screening, it still does not mean that the baby has permanent hearing loss. Reason being that most babies pass the second test and also, most times babies can have fluid, blockage, or debris in the ear that clears up on its own. So never panic if your child fails the first and second test.
It is only when further testing shows that a baby has hearing loss, then an audiologist along with an ear/nose/throat (ENT department) specialist can best determine the next steps to take. Treatment usually does depend on the type, nature and degree of the hearing loss. If the child's hearing loss is permanent, they are usually given hearing aids. Infants can be fitted with a hearing aid as young as one month of age. This proactive step and intervention will help the child as early as possible.
Genetic testing
Genetic testing involves examining a person’s DNA found in blood or other tissues for some abnormalities that are linked to a disease or condition. DNA is actually a chemical alphabet that is made up of four units that make up all of the genes or genetic material found inside our cells. Genes are important for our body’s normal development and functioning.
Usually when a mistake affecting some part or all of the genes, this can lead to an abnormal function or change in our body leading to disease. The mistake could be minute or large. These specific errors are only and easily identifiable through different types of genetic tests. They are also used to look for gene abnormalities in persons who are suspected of having a genetic disease based on symptoms the person may be having or because a close relative has a genetic disease (Family history plays critical role).
The role of family History
Knowing the Family history of a person with genetic disease is very important in diagnosis because research has shown that, they run in families. A woman with breast cancer that is not caused as a consequence of environmental factors or exposure to carcinogens will will most likely have the BRCA 1 and BRCA 11 genes.
When the she gives birth to children, say a boy and a girl. The chances that the female child would have the genes for the breast cancer is very high. if the lady ignorantly decides not to do something about it as early as possible, the chances of her coming down with breast cancer would very high.
Some individuals might have the gene that predisposes them to cancer but because they are fully aware and they avoid engaging in activities that will trigger the gene expression or activation, they end up surviving the disease. These is how important genetic testing is and the role it plays in early detection of abnormalities. So whenever you visit the clinic and the physician begin asking about your personal life and family history, the reasons above are why.
Are they always accurate?
As much as they may seem trustworthy, they are not always hundred percent accurate. Even when they positively detect a mutation (an alteration in the sequence of gene which can be caused by a host of factors), the test may or may not be able to determine when or what symptoms of the disease may show, which symptoms will occur first and how severe the disease will be, or how the disease will progress over time. Note that, for the fact that the test result is negative does not mean the individual wont be at risk for any other disease condition. Another crucial aspect of genetic testing is Prenatal diagnosis.
Prenatal Diagnosis
The word Natal means something pertaining to ones birth. So the prefix 'Pre' indicates any activity done before birth or during pregnancy. In situation where hear postnatal, it means activities done after the birth of a child. so it is safe to say that Prenatal diagnosis also known as antenatal diagnosis refers to testing performed during a pregnancy.
These testing are very important and helpful for determining the outcome of the pregnancy, it also helps them prepare for any possible issues and complications during delivery process, prepare well for future challenges that may arise. Not only that, it can also help the couple to decide whether to continue the pregnancy or not, and finally finding conditions that may affect subsequent pregnancies. One well known and common prenatal diagnosis is the antibody screening in pregnant women.
This test is also called indirect Coomb's test or indirect agglutination test and it is aimed at detecting antibodies that are present in the pregnant woman's blood (in the serum or plasma) that might cross over into the babies blood during birth. These antibodies are capable of passing through the placental barrier between the mother and the child. Upon entering the babies blood system, they cause agglutination reactions leading to destruction of the baby's red blood cells, a condition that can lead to Haemolytic disease of the new born, (HDN). We will discus this in detail in my subsequent post also, lets try and round up with this current discussion with less ambiguity. so, watch out!
Women over 35years are liable to give birth to children with Down syndrome, how true?
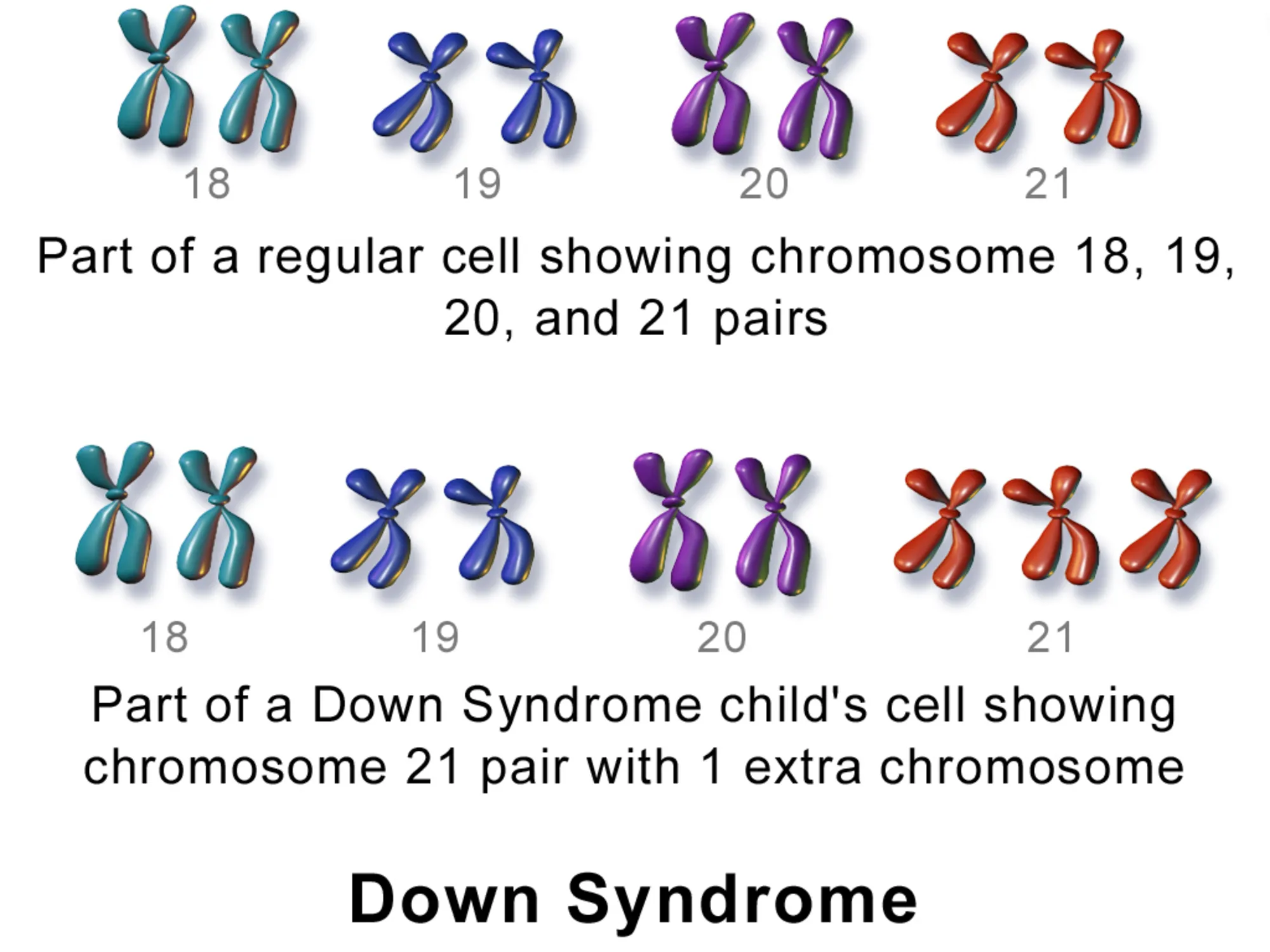
One of the common reason for prenatal diagnosis is the mother’s age. Report has it that, women who will be over 35 years of age as at the time of delivery have a higher risk of having a child with a genetic condition such as Down syndrome (a genetic disorder caused by the addition of extra chromosome 21, that is, three copies of chromosome 21 to the one already in existence, XXX aka Trisomy 21) and as such prenatal diagnosis should be offered to them. This though does not hold in all cases but the chances are their and as such diagnosis would be very necessary to be of the safer side.
Conducting genetic testing or screening is one sure tool that will help the physician to know the state of the baby and also guide their decision. In situation where it is not done, the consequence can be the birth of a child with mental retardation.
Back to our discussion on different kinds of prenatal diagnosis, there are several types of prenatal diagnosis that are available besides the earlier explained indirect coombs test. These are available depending on how far along the pregnancy is and what type of disorder is being tested. Also note at this point that, these test though have been shown to be accurate to an extent, they are not used in isolation to confirm diagnosis, case in point, down syndrome cases.
Note that, when the combo of maternal serum Alpha Feto-protein (AFP) concentration in addition to the age of the mother and finally the along with the hormone markers in the mother's serum - (estriol and human chorionic gonadotropin, hCG - the common pregnancy hormone you know), together can provide a more sensitive serum screening test.
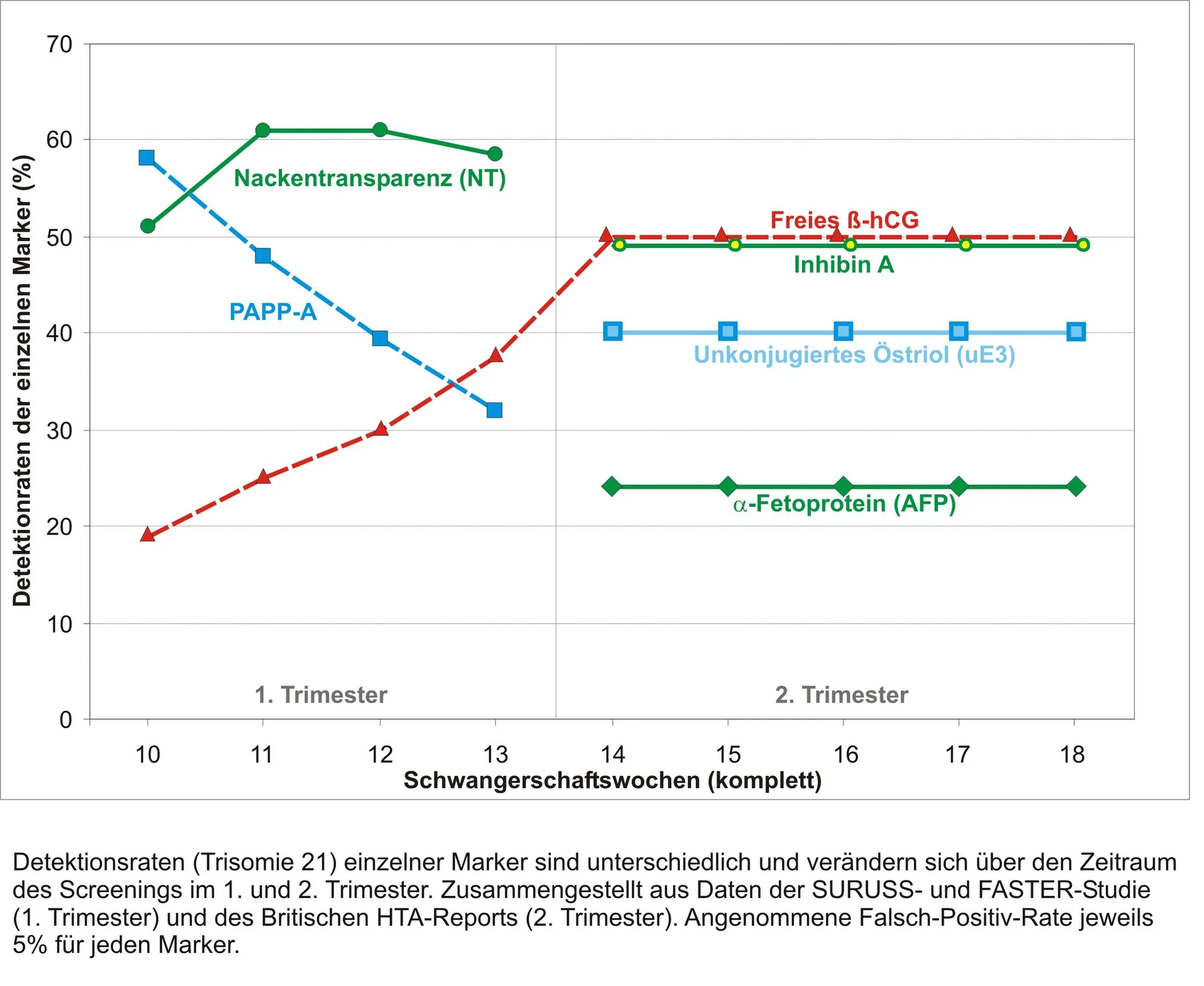 Detection rates of single markers in antenatal Down syndrome screening
Detection rates of single markers in antenatal Down syndrome screening
Low levels of MSAFP and estriol, along with high levels of hCG usually suggest an increased risk of Down syndrome. Report have shown that low levels of all three markers is a probable indication of increased risk of Edward syndrome (trisomy 18). The inclusion of a fourth marker known as inhibin-A, in the maternal serum screen further improves the accuracy in predicting risk of babies that might have Down syndrome.
Some of the screening test includes include Chorionic villus sampling (CVS), Amniocentesis, Periumbilical blood sampling (PUBS), and fetoscopy. We will briefly only talk about the two most common procedure - CVS and Amniocentesis.
Amniocentesis and Chorionic villus sampling
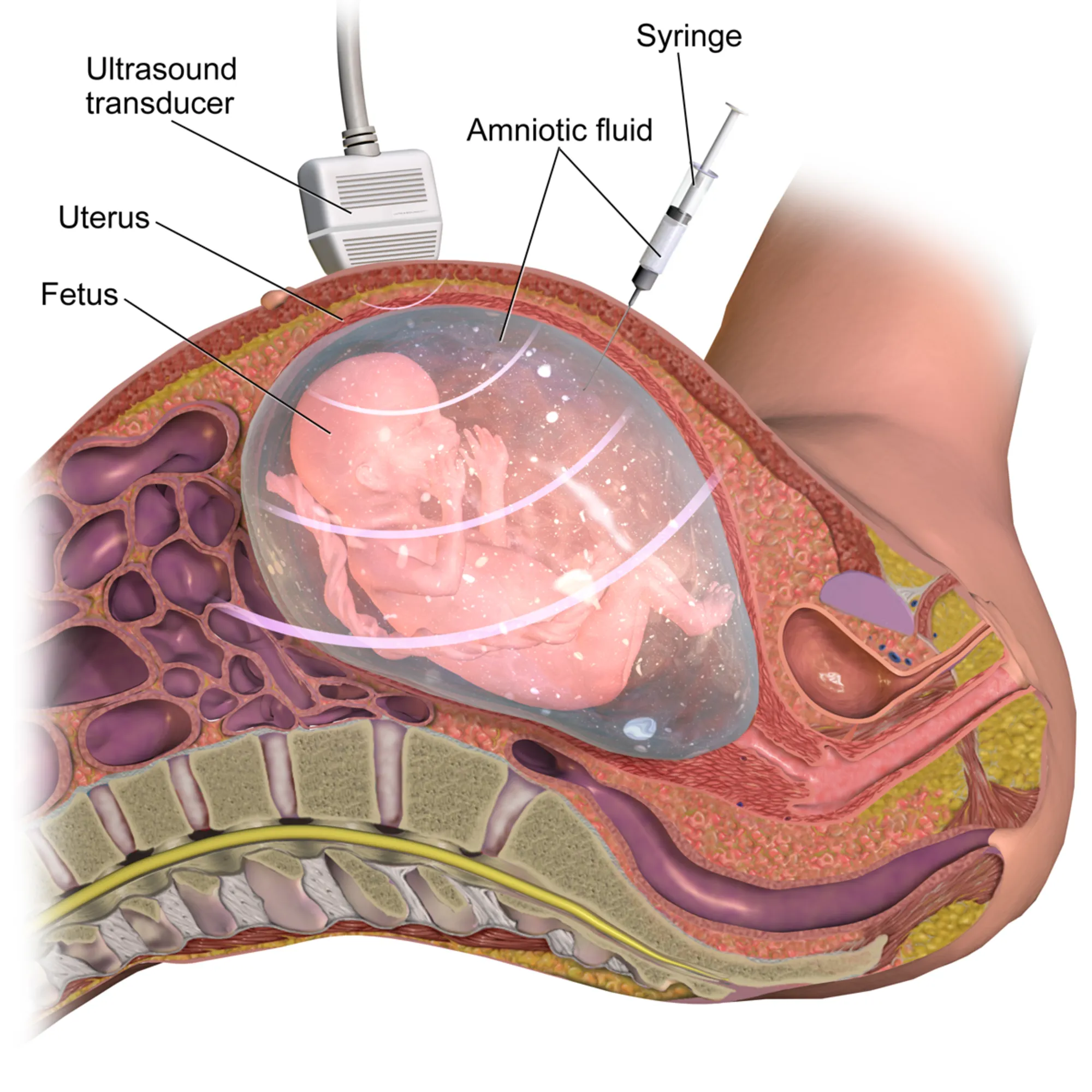
Very importantly, amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling are both highly invasive procedures that carry a risk of miscarriage if care is not taken. Amniocentesis has to do with the removal of a sample of amniotic fluid from the uterine cavity by a syringe through the abdomen. It is usually done at 15 to 20 weeks gestation (pregnancy).
On the other hand, in CVS, the baby’s cells are removed from an area around the baby known as the chorion with a syringe inserted through the cervix or abdomen. It is performed much safely at about 10 - 13 weeks' gestation.
The Amniocentesis and CVS samples collected, is made up of the newborn's cells which are later analyzed in the laboratory. Information gotten from the test will go a long way in identifying any possible genetic abnormality. If the case is a very serious one, then, the result will also determine the next line of action to be taken by the physician.
Current available methodologies for genetic and newborn screening
Technology is advancing, so also are modern and advanced way of solving problem are. Today there are better methods that have been developed in testing for any abnormality. Usually, the test employed depends on the type of abnormality that is being measured. The major ones are: molecular testing, biochemical testing, and lastly cytogenetic testing,
like I earlier said, they are available depending on the abnormalities. The cytogenetic testing is done to detect abnormalities in the chromosomes (threadlike structures that houses the genes at different particular points called locus).
The Biochemical testing is done to detect abnormalities in protein structure and functions while molecular testing is done to detect any change in the structure of the DNA sequence.
I will conclude here by saying that without effective screening of newborns and also prenatal diagnosis, the tendency to have a surge in cases of malformation and disabilities in children is high. When we have an in-depth knowledge of the principle genes is the first step in genetics. When we now take a further step to understand their various roles in diseases pathogenesis and how they interact the environment in which they are will help go along way in improving diagnosis and treatment of several genetic diseases.
Genetic testing is a very important diagnostic tool that has helped a lot of families and individuals. Even though there are still cases, the incidence so far from reports are on the low side. The few cases being reported are usually as a result of maybe negligence and nonchalant attitude on the part of the parents.
Though these testing can be very expensive as not all can afford it. In some continents, poverty, illiteracy, religion, culture and beliefs are some of the mitigating factors against newborn screening and also genetic testing. This only calls for more public health enlightenment programs especially in developing countries. It is always advisable to subject ourselves to genetic screening once we discover that a particular genetic disease runs in the family. This will help offer good prognostication. Thank goodness for evolution and scientific advancement!
Until I come your way again, stay awesome!
Thanks for reading.
References
•CDC Grand Rounds: Newborn Screening and Improved Outcomes •First-trimester biochemical markers for Down syndrome •Risk of a Down syndrome live birth in women 45 years of age and older •Biochemical markers of trisomy 21 and the pathophysiology of Down's syndrome pregnancies •First trimester biochemical screening for Down's syndrome in singleton pregnancies conceived by assisted reproduction •Biochemical Screening •Genetic screening - A primer for primary care •Genetic Screening and Diagnosis- an overview •Newborn hearing screening •CDC- Newborn Hearing Screening: Infants and Babies’ Hearing Can Be Checked •Hospital-based universal newborn hearing screening for early detection of permanent congenital hearing loss in Lagos, Nigeria
Return from Genetic testing and Newborn screening: What if there was none? to cyprianj's Web3 Blog