Welcome to the 8th episode of our interesting workshop series where we bring you live microscopic images of those organisms and parasite that are responsible for some of the diseases affecting humans. Today, we will be discussing about the fungi that was isolated from a patient. Needless to say, we will be visiting mycology for the very first time since this workshop series started. Sit tight and enjoy the read, you have one or two things to learn from here.
As usual, we will begin with an introduction to mycology, how they live and affect us as humans. What makes them thrive in the environment and why are humans infected. Our focus will be on one of the fungi of clinical significance - Candidada albican. All these and more, are what we will be discussing today.
Introduction
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms with diverse species. You practically find them almost everywhere. The major species are the moulds, yeast and mushrooms. Thy are natural heterotrophs (organism that depend others organism for food since they cannot produce theirs by themselves).
They mostly reproduce using spores and they have extensions that look like thread and these are referred to as hyphae. A characteristic feature easily seen when they are viewed under the microscope. The major reason why they are unable to produce their own food is because they lack the pigment known as chlorophyll. They thus depend on other organisms and to some extent, they can be parasitic in nature.
Their reproduction pattern could either be sexual, vegetative or asexual. In sexual pattern, it involves the use of ascospores, basidiospores, and oospores to produce another generation.
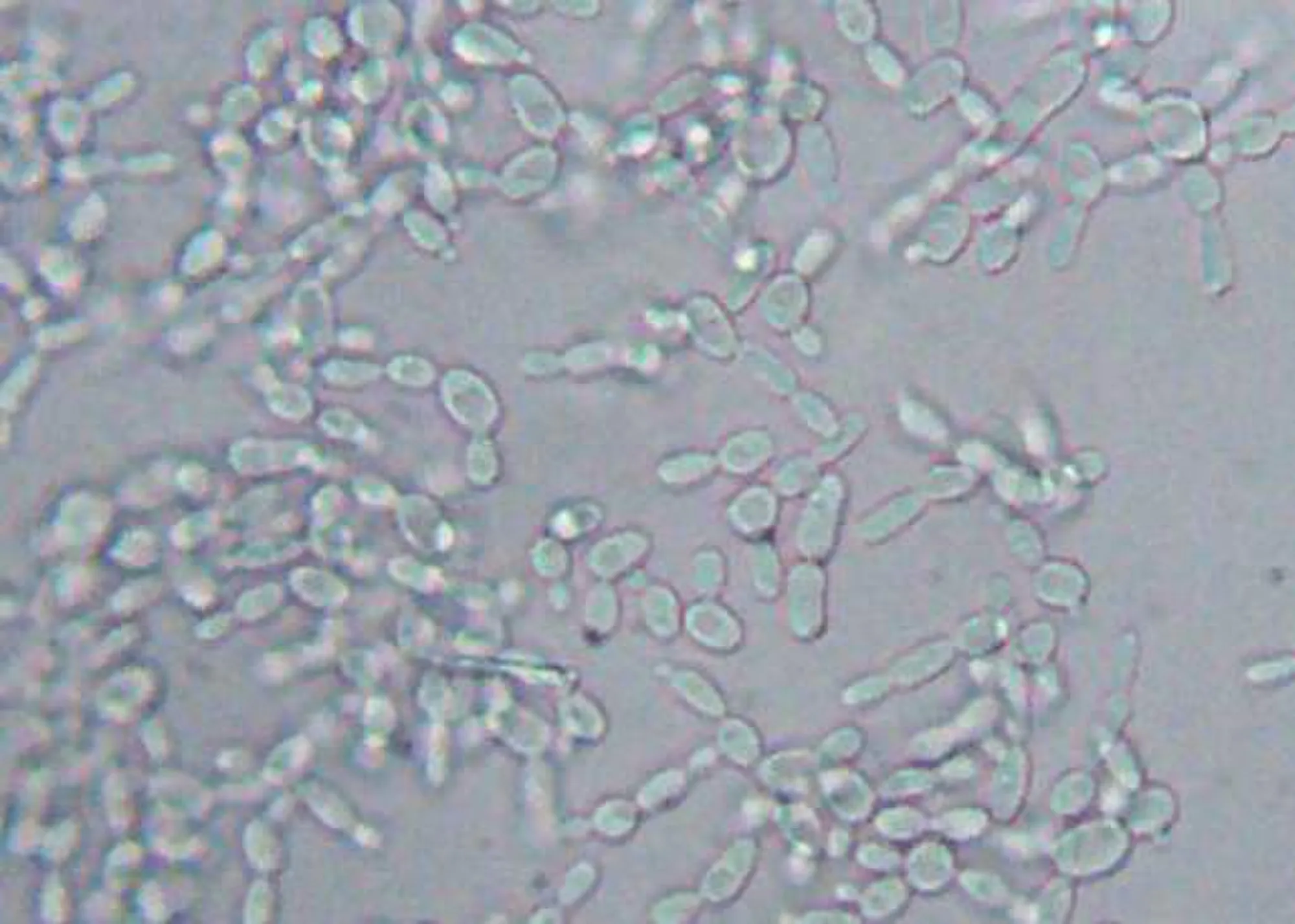 Wet mount showing several yeast like budding cells, identified as Candida
Wet mount showing several yeast like budding cells, identified as Candida
On the other hand, the asexual reproduction pattern is commonly through the process formation and use of spores called conidia or zoospores, or the use sporangiospores. The third form reproduction, though still asexual in its strict sense is budding, fragmentation and fission.
Budding which occurs mostly in yeast cells, is always clearly seen as yeast cells, case in point Candida albicans The buds develops on the fungi which later matures into a full yeast cell. They have the ability of producing many buds on their surface through which they multiply by nuclear division.
There is no need boring you with all the intricacies about the methods, since our focus is on yeast cells, the like of candida albicans. Fungi infection can prove very difficult to treat due to antibiotic resistance. Let's briefly talk about the one common type of fungi that is commonly associated with infections in individuals - Candida albicans.
Candida albicans is the most common fungi infection that causes the disease known as Candidiasis. The fungi can be normal that are found on various parts of the human body including the skin, gut, vagina, mouth, throat etc. They live in these places with no harm in the host body. Problem ensues when they overgrow and penetrate other areas of the body like the blood, brain etc. Candidiasis is more common in women than men.
Clinical Diagnosis of Candida
Generally, to diagnose infections caused by fungi, you will first need to do a wet preparation to visualize them. Depending on the sample collected, if it is urine sample, you will need to spin it first, to as to concentrate the urine constituents.
Remember that we have earlier before now explained urine deposit. Fungi in urine is a classical example of organized urine deposit. To a a basic understanding of urine deposits, you can read this post here - Medical laboratory workshop Episode 5: Urine deposits can predict your health status.
Just like every other microorganisms, candida is best viewed under the microscope for good characterization and observation. For now, we are more interested in viewing the fungi. Since we are examining the urine, it is always better to concentrate the sample by spinning it using a centrifuge.
After spinning, you decant the supernatant fluid and the re-suspend the filtrate by gently tapping the tube. Place a small drop of this filtrate on a clean grease free slide and cover with a coverslip. You then proceed to view under the microscope using X10 objective less to focus and X40 to view the fungi. Let's discuss our microscopic findings.
Results and clinical significance of candida albicans in urine
The analysis of the urine of a young female revealed the presence of numerous fungi in the urine sample as can be seen in the image below.
Make no mistake about it, most fungi have a characteristic shape of being oval. They measure about 2-4um in diameter. Their yeast form is always very visibly oval. They could also be in the form of hyphae or pseudohyphae. Candida specie of fungi reproduce vegetatively through budding. We will carefully study each of the images to buttress some of these points as we continue.
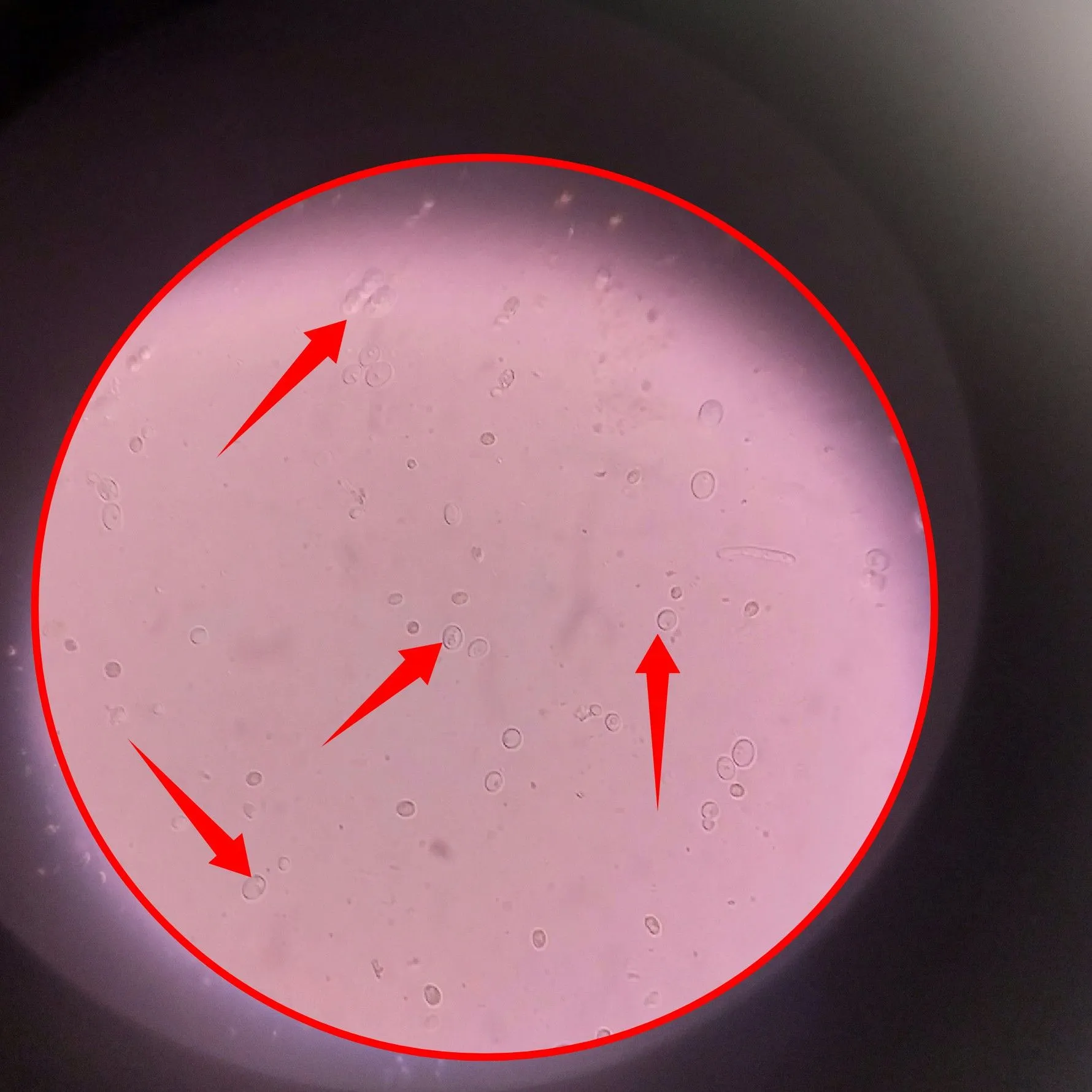
In the meantime, the image directly above reveals almost but not all of the different forms of the Candida you would expect to see when you view them under the microscope. We will make do with the ones we were able to identify.
As earlier said, most candida specie of fungi reproduce vegetatively through budding. This involves the splitting of the cells into two through a process known as nuclear division. The image below reveals this process.
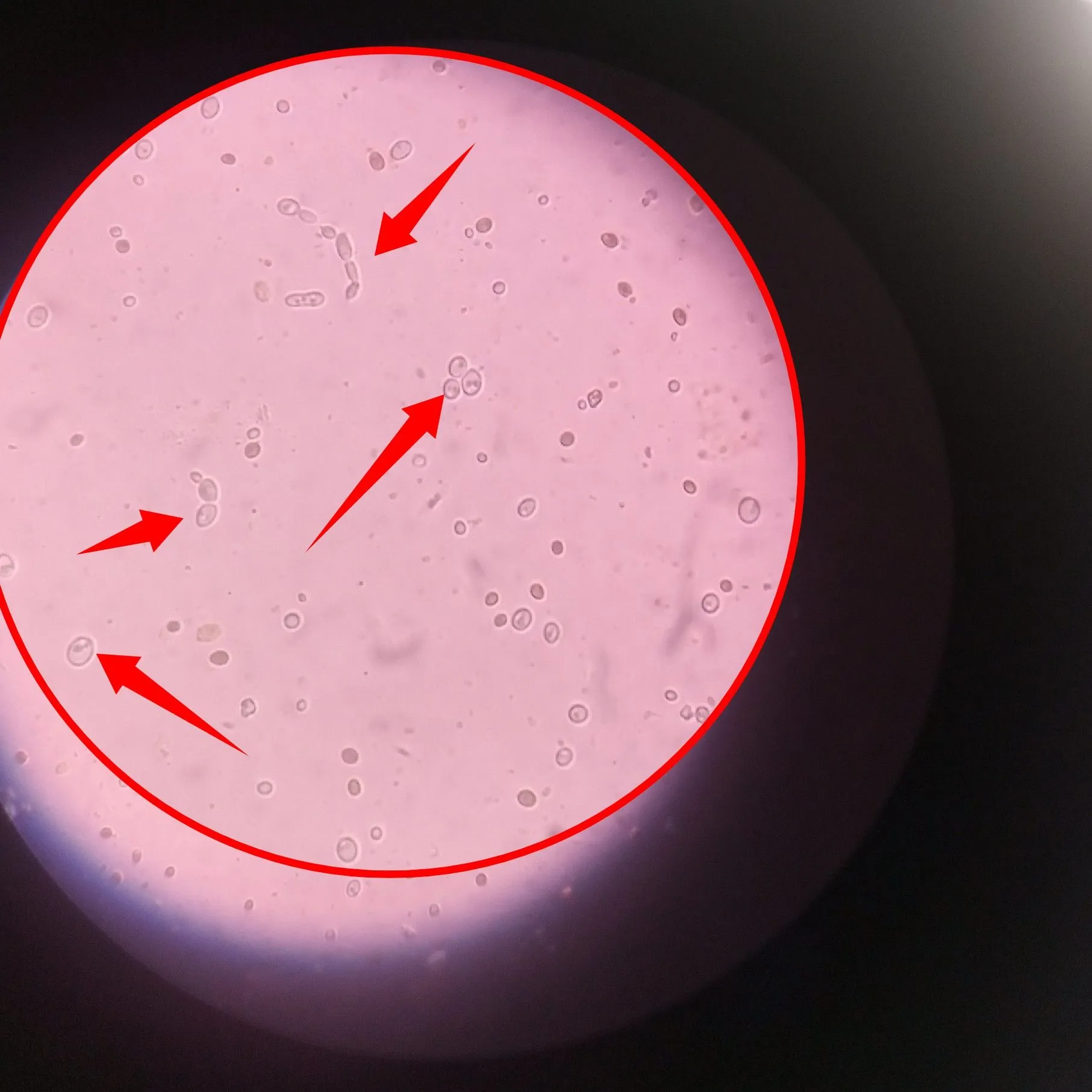
The pointed structure in the image directly above is an actively dividing cell almost at the last stage of nuclear division. You can also refer to that stage as a budding fungi. Regardless we will reveal a more definite image later. Our next target is to locate a hyphae and fortunately, we are able to find more than one.
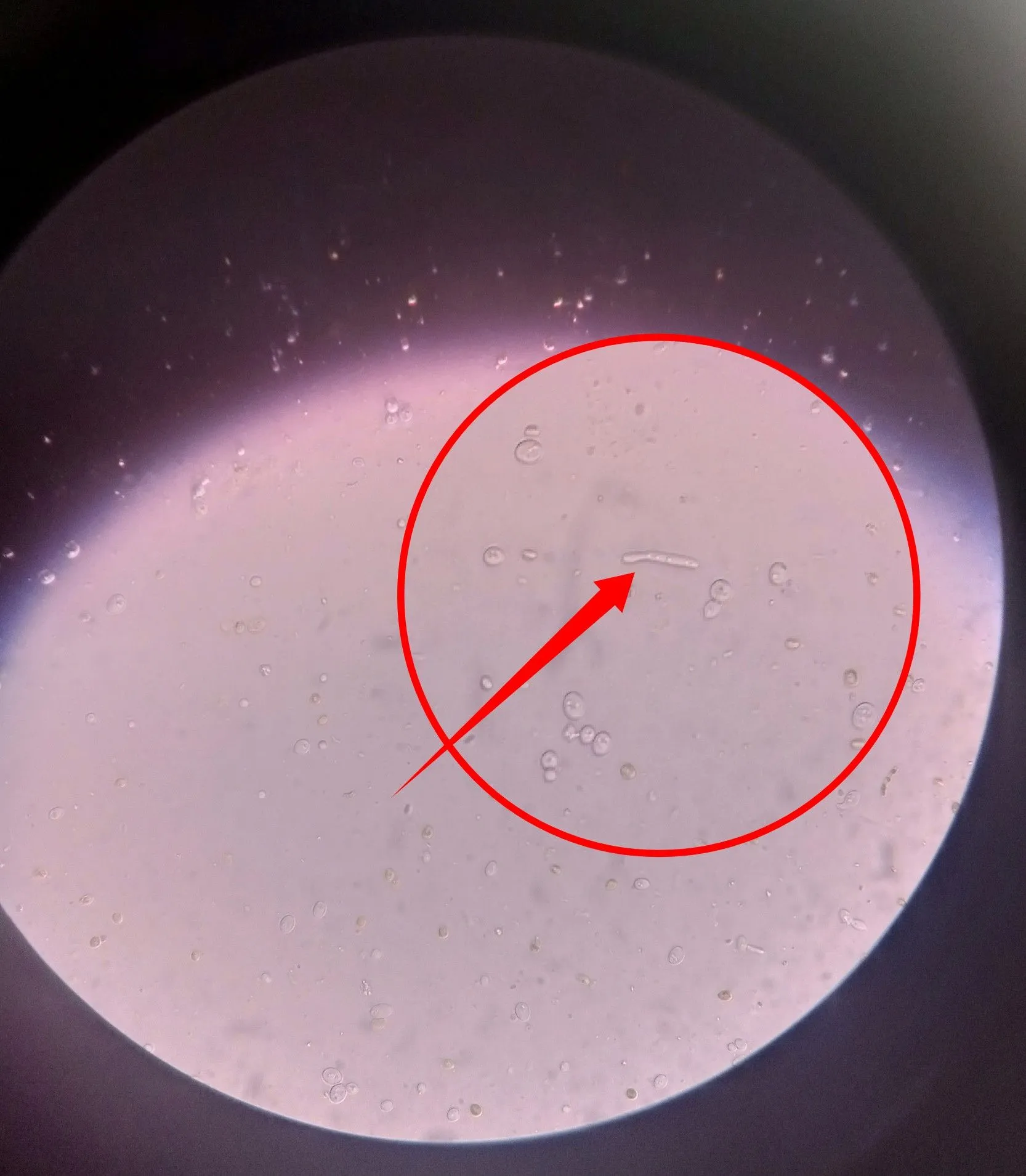
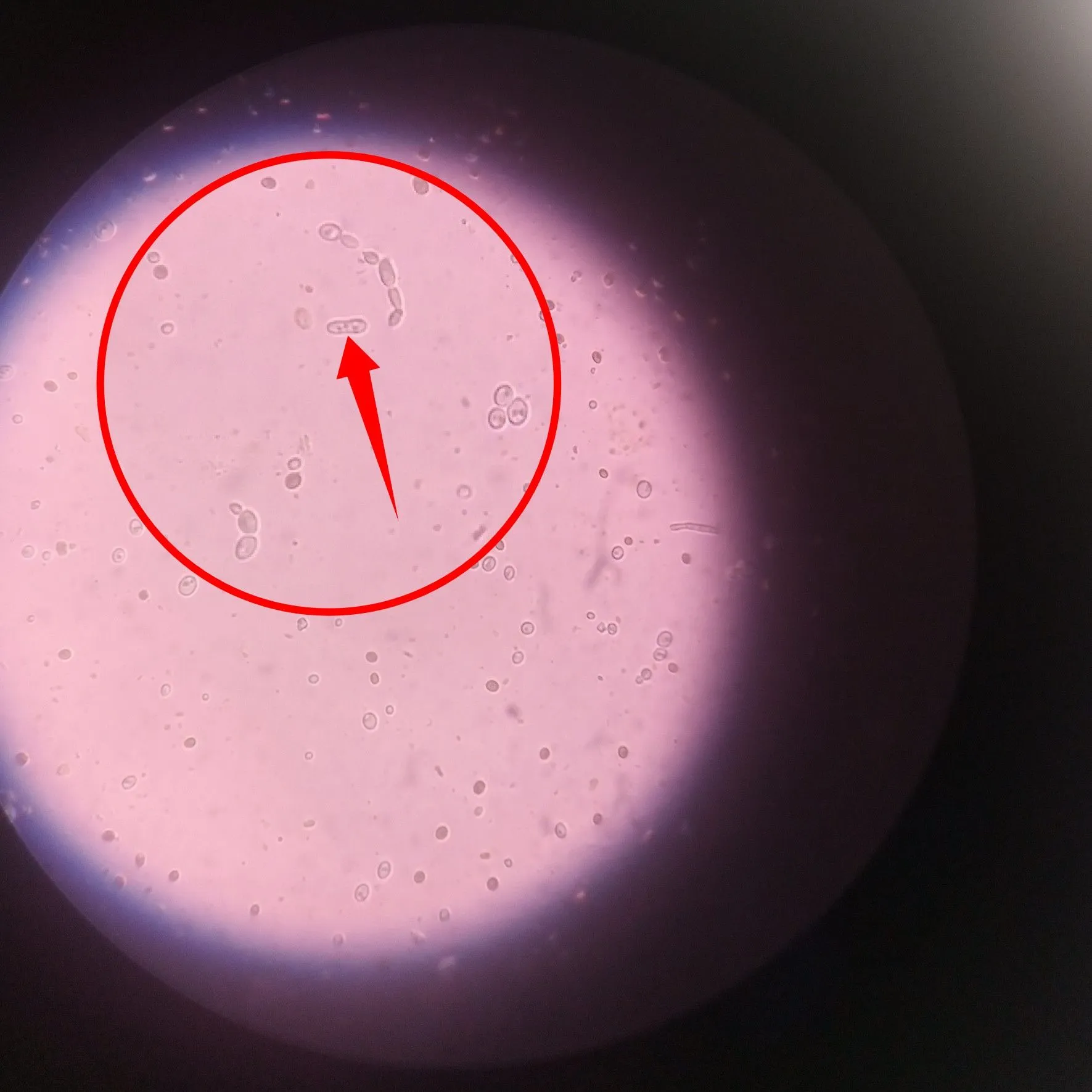
Observe closely the image directly above and below. That is a clear microscopic image of a fungi hyphae. The hyphae is a very important part of a fungi because it serves the role of a nutrient absorber.
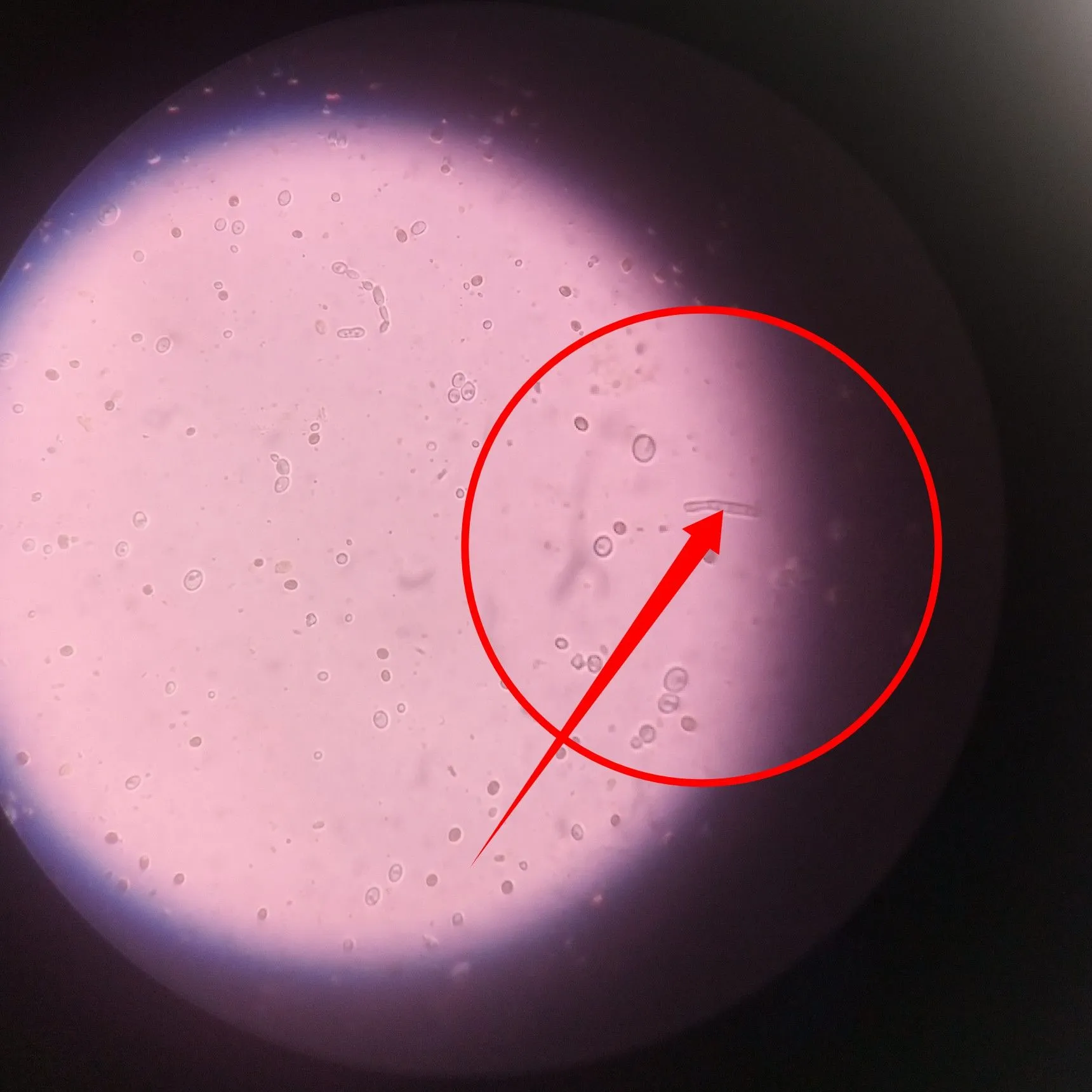
It absorbs nutrients from the surrounding environment required by the fungi for survival. It also houses the genetic machineries of the fungi, i.e the nucleus. Next we will now have a closer look at is a budding candida.
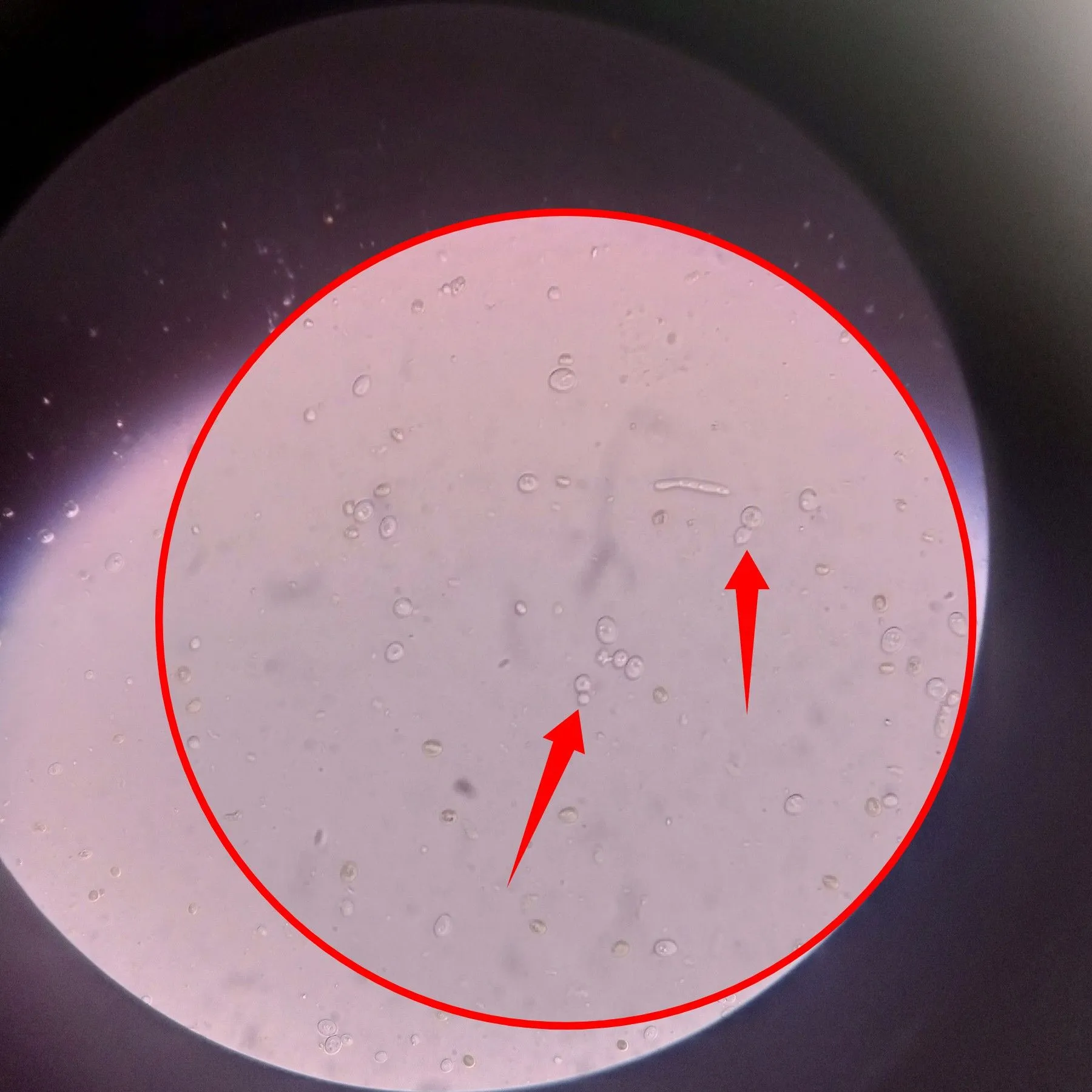
The pointed arrows in the image above reveals different budding candida. This represent part of its growth pattern. In a nutshell, always remember that candida albicans have three main growth vegetative growth patterns - yeast form, pseudohyphae and true hyphae. For this reasons, candida albicans is refered to as a pleiomorphic fungi (an organisms that has different structural patterns during their life cycle). This phenomenon is known as pleomorphism
Candida albicans become problematic we when they are overgrown or are found in areas of the body that are meant to be sterile. Just like we earlier learnt, naturally, they are part of our existence as humans and they tend to live as normal flora. Their overgrowth could cause a disease known as Candidiasis
They can infect the blood, and when the yeast form of this organism renters the brain through the blood, they can cause memory losses. This is particularly associated with the invasive types of candida.
Treatment can be easily achieved so long as it has not develop resistance to the common antifungal drugs like the -azole group. Even though genital infection with candida can happen to both male and females, it very common with females due to the susceptibility of the female genitals to infections. In this case, it refered to as Vaginal Candidiasis.
Probably you are wondering why it is common in women, the reason is because of the anatomical position of the vagina and how easily accessible they are. The common symptoms experienced by individuals with Candidiasis is irritation of the genitals, inflamed genitals, itchy scratch that becomes intense during heat and sweating.
Another significant sign is the colour of the vaginal discharge that looks whitish to yellow in colour. This discharge is usually very thick. When you experience this symptoms, do not hesitate to visit the nearest hospital for treatment.
Conclusively, maintenance of proper Personal hygiene is of paramount importance in the prevention against Candidiasis. Candidiasis is easily preventable, don't fall victim.
References •Sexual reproduction in the Candida clade: cryptic cycles, diverse , and alternative functions •Introduction to Fungi •How fungi are constructed •Candida Albicans- An Overview •Treatment of vaginal infections: candidiasis, bacterial vaginosis, and trichomoniasis
Return from Medical laboratory workshop Episode 8: Clinical evaluation of vegetative forms of Candida albicans responsible for candidiasis in humans to cyprianj's Web3 Blog

