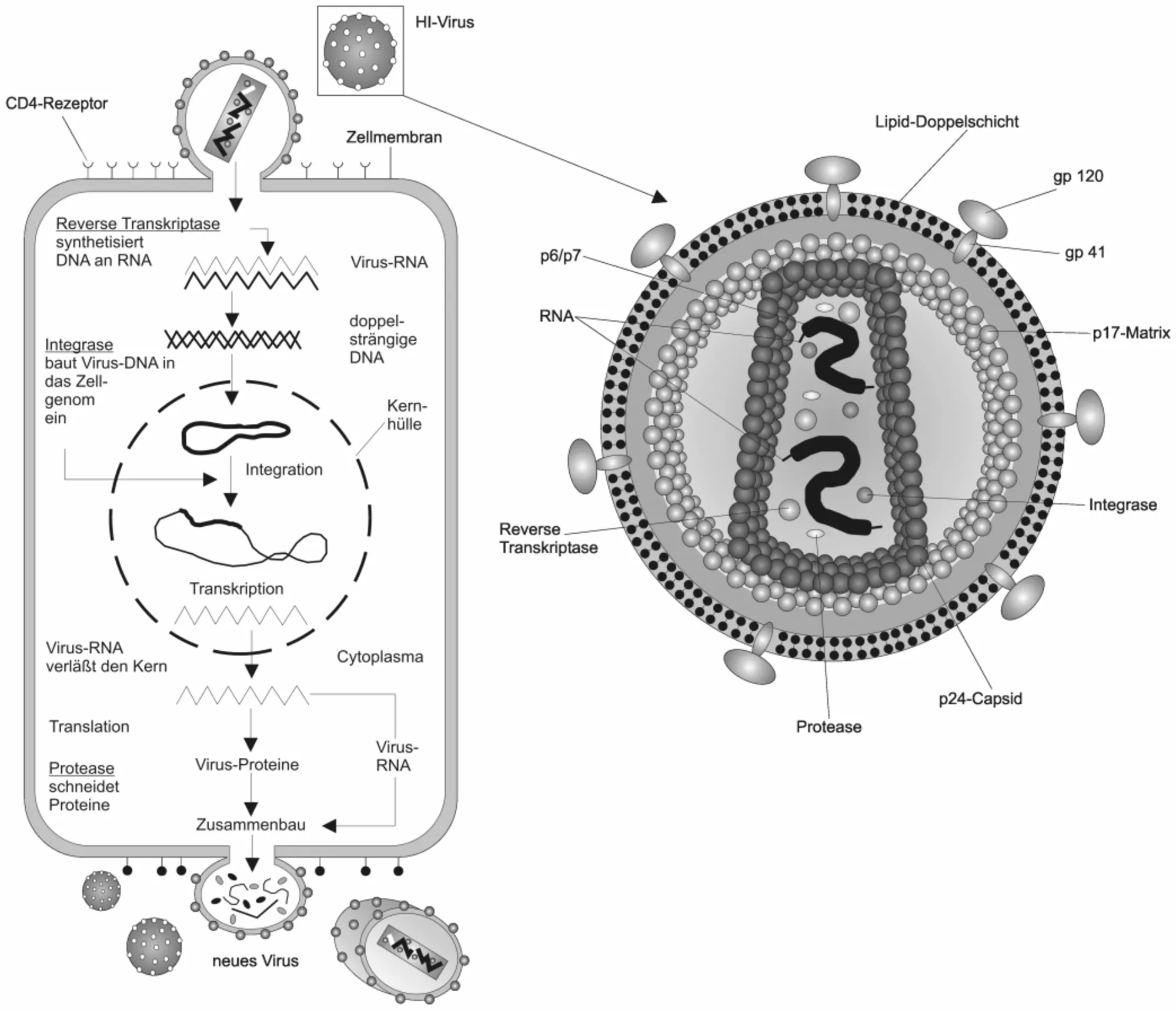
HIV infection is no longer a new thing because virtually every individual can to some extent talk about this disease. The reason for this, is not far fetched and it is simply because of the massive globally publicity the disease attracted. The campaign against this virus has been tremendous over the years and till date, the awareness and sensitization still continues.
 Jennifer Jako, activist living with HIV-AIDS in 2012
Jennifer Jako, activist living with HIV-AIDS in 2012
Jennifer Jako, living with HIV/AIDS, holding a sign that states "No Child Born with HIV". Jako has a healthy daughter because she had access to prenatal care and antiviral medications during pregnancy.
It is undoubtedly true that research has gone so deep into the discovery of the ultimate cure to HIV infection. HIV in its own right has proved very stubborn when it comes to cure. The way the virus operates makes it difficult to be fully eradicated. Its ability to camouflage and evade the human defense mechanism (white blood cells) gives it that advantageous position over any treatment you can think of.
Just to refresh our mind, Human Immune Deficiency Virus (HIV) is one of the most dreaded viruses that attracts global attention. It is the etiologic agent of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS Related Syndrome or Complexes (ARC). The virus was recognized and documented in the USA in Sanfrancisco in 1981.
HIV was diagnosed in Africa (Kenya) first in the year 1984 and in Nigeria the year 1986 from a sexually active thirteen year old girl. Its major mechanism of action just like other viruses is to mimic its host defense mechanism, destroy this defense mechanism (especially the CD4 cells) and consequently find its way into the genetic machinery (the DNA). Once in the DNA, they then take over the genetic functions and thus produce million copies of its RNA. The new virions in turn infect other healthy defensive cells of the host and causing havoc in the process.
The evil cycle, if not halted continues in the host until they totally destroy their host. Of course, if you are the one, invading a host, your target would be to take over the seat of power by weakening and removing greater threat or anything that tends to oppose your mission. Yeah, you are free to liken the action of HIV to the mission of Putin in Ukraine. Taking over Kyiv, the seat of power will sure lead to the fall of Ukraine.
Due to never relenting research to find HIV permanent cure, this led to the development of Antiretroviral drugs therapy (ART). These drugs basically do not cure one that is already infected with HIV rather, it only helps to inhibit and reduce the rate at which the HIV damages the human cells (CD4 cells). These drugs all have different mechanism of action based on the particular structure of the HIV they attack.
Why it is importance to remind us that as much as there have been progress in ensuring that ultimate cure to the endemic virus is found is that, some people still doubt the existence of this virus. Out of sight is out of mind, well not in the case of HIV. Reports has shown that
About 1.2 million people in the United States had HIV at the end of 2019, according to the CDC, with more than 36,000 people being diagnosed in 2019. The World Health Organization says 37.7 million people in the world had HIV in 2020.
It is not surprising to see the increase in number of infected individuals because most people live careless lives with the wrong assumption that HIV is no longer in existence and also, most have laxed attitude when it comes to taking precautionary measures in protecting themselves against the virus. For the fact that this virus is easily gotten through sexual contact, it makes it more difficult to curb because many young individuals still find it very difficult abstaining from unprotected casual sex.
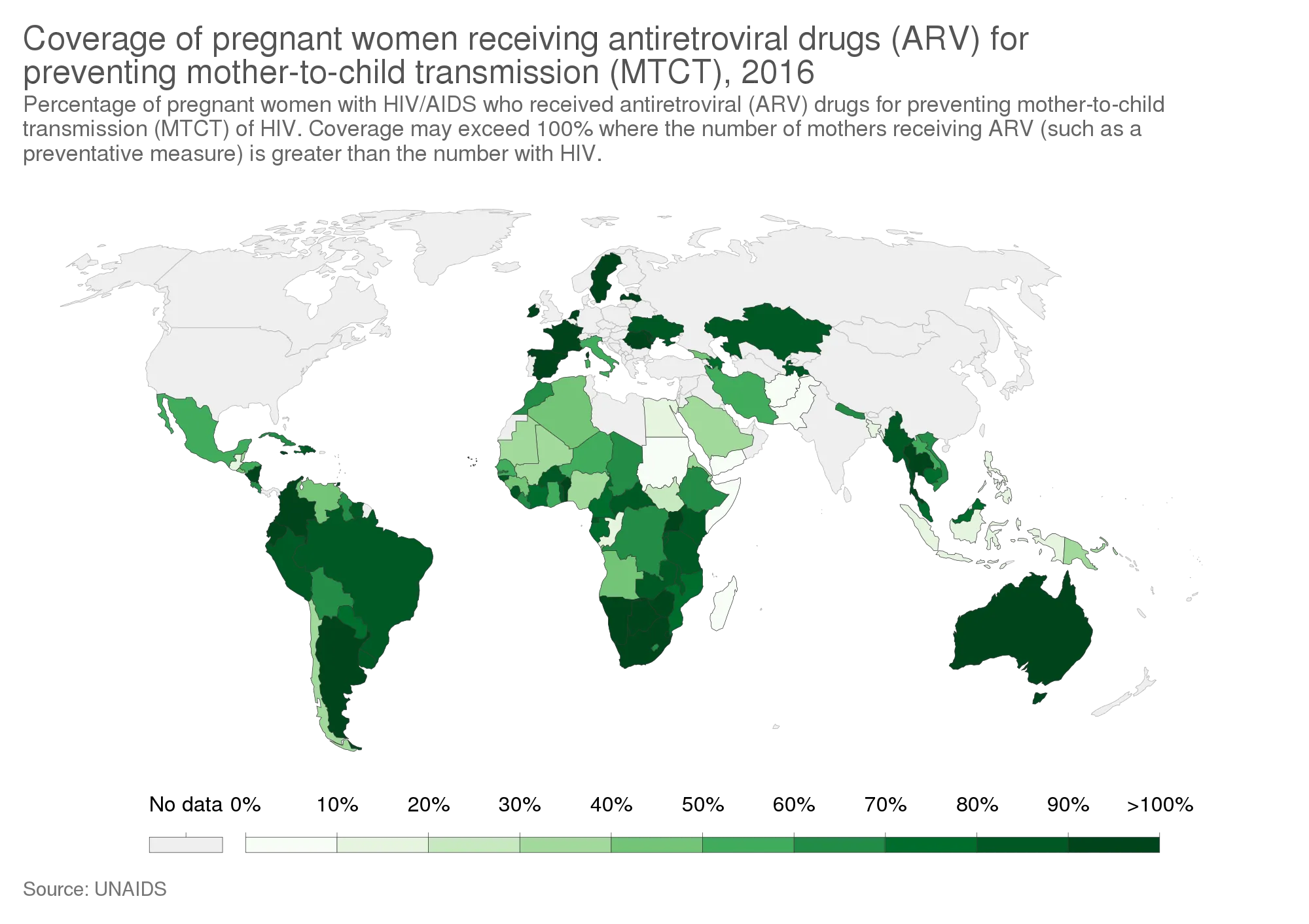
Of more concern is maternal transmission of this virus to neonates mostly during the process of child birth. This poses serious issue and threat in the health sector and this is why a lot of campaign against mothers not going for antenatal visit to the hospital have been made. It is through the antenatal testing that a pregnant woman with HIV infection can be detected.
Early detection of HIV during ante-natal visits by the pregnant women makes prognostication easier because they are placed on antiretroviral therapy to help reduce the viral load in the pregnant mother. When the viral load are reduced to the point that they are undetectable in the blood system, it drastically reduces the probability and chances of the newborn being infected with HIV during delivery. This is the major goal of retroviral therapy besides being aimed at helping the pregnant live a healthy and normal life.
As usual, we will begin by giving a summary of the research work through abstract.
Abstract
Seroprevalence of HIV among pregnant women attending antenatal clinic in Kumo General Hospital was studied in 350 sera. The sera were obtained from women of different age group, occupation, social background including tradition (by tradition we mean people’s ways of life common in that locality). Screening was carried out using Abbot determine test strips and Gene 11 HIV 1 and 2. The Bio-data information of the women was gathered through questionnaire administration. Out of the 350 sera collected, 12(3.4%) were reactive for HIV. There was high prevalence among age group 21-30 (2.1%) followed by age group 11-20 (0.9%). High prevalence was also observed among the unemployed pregnant women (2.1%). Women who had no risk factor were also noted to have had high prevalence (1.7%); Spouses of seropositive pregnant women and those with no risk factor had 42% and (33%) prevalence respectively.
Keywords: Prevalence, Women, HIV, Pregnancy
overview
HIV infection among pregnant women has been identified as a major cause of Paediatric HIV/AID which leads to death that has now become a global concern. Infection with HIV is now pandemic with over 39.5 million people currently infected world-wide of which over 2.2 million are below the age of 15 years.
The study was therefore designed to determine the prevalence of HIV infection among pregnant women attending antenatal clinics in Kumo, Gombe State. Findings from this research work can help inform health care institutions, most importantly in Nigeria so that adequate measures can be taken to reduce drastically the rate of transmission of HIV to newborns.
Research methodology
Sample collection and processing: Five milliliters of blood was collected from each subject allowed to clot and the serum was separated by centrifugation for 5 minutes at 2500rpm. A total of 350 sera were obtained, they were heat inactivated at 56OC for 30minutes and stored at -200C, ready for laboratory assay. Their bio data was collected with a well structured questionnaire after ethical and consent approval.
Laboratory Sample Test: The sera (the liquid part of blood derived by allowing non-anticoagulated blood to retract in a plain tube) were screened using Gene II HIV-I and HIV-2. It is a rapid enzyme immunoassay for qualitative detection of antibodies to human immune deficiency virus types 1 and 2 in human serum or plasma. The sample were further screened with the Abbott determine test strip ( a further quality check).
Note that sera is best used instead of plasma (liquid part of blood from anticoagulated blood sample) because the antibodies to the HIV are mostly concentrated in the sera. Secondly, sera is purer than plasma since it does not contain impurities that may interfere with the accuracy of the result. Moreover, ELISA is a very sensitive procedure that can detect HIV presence in an analyte of interest.
The Gene II HIV-1 and HIV-2 has presented 100% sensitivity on true HIV positive and seroconversion panel with specificity of 99.8%. All test procedures and interpretations of results were carried out according to the manufactures instructions and specifications. Observing strict adherence to the manufacturer's instruction ensures accuracy and precision of results gotten. At this point, quality assurance is of utmost importance.
Results and findings
All sera samples were reactive to only HIV-1. This implies that HIV-1 type virus was responsible for their HIV infection. This simply rules out the chances of cross reactivity.
Table-1: Overall Distribution of HIV among the subjects

Table 1 above shows the overall distribution of HIV among the pregnant women screened. Out of the 350 samples, 12(3.43%) were reactive to HIV while 338 (96.57%) were non-reactive.
Table-2: Age Distribution of HIV among the pregnant women
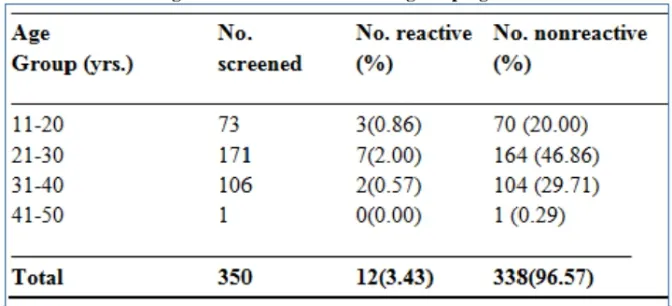
Table 2 presents the age distribution of HIV among the women. Age group 21-30 years had the highest reactive number (2.0%) followed by ages 11-20 with 0.86% while the age group 31-40 had the least with 0.57%. There was no reaction in age group 41-50 years
Table-3: HIV distribution among the women based on their Educational Status
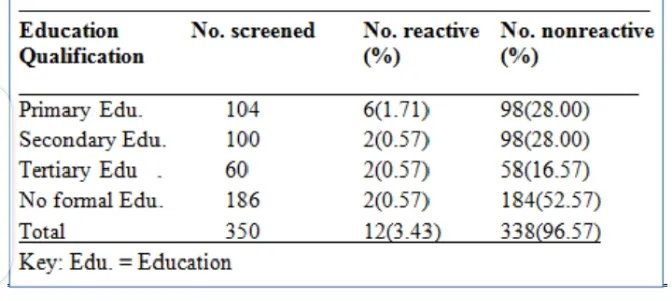
Table 3 shows the educational status of the pregnant women. The highest reactivity came from women with primary education with 6(1.71%). The secondary, tertiary and informal education had equal reactivity of 2(0.57%).
Table-4: Occupational distribution of HIV among the pregnant women
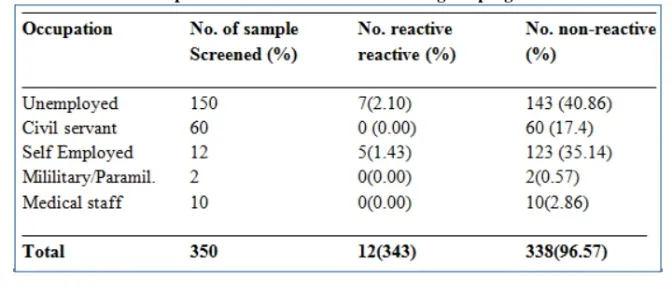
Most of the women (186) had no formal education. The occupational distribution of HIV among the pregnant women screened is presented on Table 4. The unemployed had the highest reactivity with 7(2.1%) followed by the self-employed (5(1.43%) while the civil servant, mechanical staff and military/paramilitary had no reactivity (0.00%) (Table 4)
Table-5: HIV distribution among the women based on risk factors
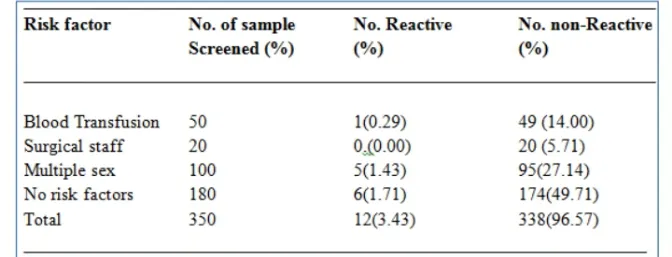
Table 5 presents the distribution of HIV infections. Based on the risk factors among the women. The no risk factor group (186) had the highest reactivity with 6(1.71%) followed by the multiple sex with 5(1.43%) while the blood transfused women had the least with 1(0.29%).
Discussion
Previous studies conducted on HIV have shown that the disease is now endemic in the country. From the first single case diagnosed in 1986 in the country, the disease has assumed an epidemic status. This study showed the presence of HIV infections among pregnant women in Gombe State. The 3.4s% prevalence rate obtained in this study although seems to be low, is of great medical significance since the disease is a dreaded one. If these individuals are not managed adequately, the chances are high that they will spread this virus and this will only end making eradication difficult. Zero global infection among individuals is the goal of WHO.
The 3.43% prevalence is in line with the report of who got 3.5% prevalence among pregnant women in Sokoto. The case of HIV infection in pregnant women is a potential case in offspring and children as 20% of infants born to HIV positive parents are HIV positive. Since most of the women have no formal education, their infections may be due to lack of sufficient knowledge of the disease or lack of good medical facilities to control the transmission and spread.
The age distribution showed that ages 21-30 years had the highest prevalence (2.0%). This figure is in line with the report of Menakaya, (1999) who reported same figure in Abuja. The infections of this age group may be attributed to active involvement in social life styles, some of which involves having unprotected sex and prostitution early in life (Table 2).
The prevalence among the primary educated women may be attributed to the danger of low level of education in the society and also the high prevalence among the unemployed may influence them to have premarital sex or prostitution in order to survive.
Undetectable means Untransmittable
Recall that, the goal of ART is to reduce the viral load of HIV to the barest minimum in the individual infected.
The point at which a viral load is classified as being undetectable may vary across different countries depending on the tests available. But so long as your viral load is under 200 copies per millilitre, you’re considered virally suppressed and unable to pass HIV on.
There is an inverse relationship that exist between the HIV viral load and the human CD4 cells. A drastic reduction in the number of HIV viral load is a good indication that the retroviral drugs are very effective and this is supplemented with an effective increase in the number of CD4 cells count. If one has an undetectable level of HIV viral load, the individual cannot infect another person through any means. This is one of the interesting thing that antiretroviral therapy has been able to achieve till date.
In conclusion, this study has revealed the presence and continuous spread of HIV among pregnant women which may result to Paediatric and infant HIV and AIDS. To prevent further transmission and spread, it is strongly recommended that all medical centers and Hospitals should be properly equipped with more sensitive modern equipment and diagnostic techniques.
The public enlightenment campaigns awareness must be continued and also stepped up since it has been generally observed that individuals have developed cold feet when it comes to taking preventive measures against the virus. If maternal fetal transmission of this virus is not curbed, the imminent danger it poses can be devastating to the general populace.
We all can be proponents and ambassadors of antenatal testing in any community we find ourselves by encouraging pregnant women to go for antenatal testing if they are not already registered in any healthcare facility.
HIV is still very much around, play safe and if you must do the act, use effective protection. Remember, COVID is also still much around, observer every protective measures required.
This research work is under Public Domain and can be accessed here
Until I come your way, stay safe.
References
- Gallo, R.C. (1998). Detection and Isolation of Cytopathic Retrovirus (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS. Science. 244 (4648): 500-503.
- Ukwandu, N.C.D. and Kudi, A.A. (2002). Human immunodeficiency and sexually transmitted disease. Journal of Medical Laboratory science, 6; 103-111.
- World Health Organization (2001). Progress in HIV/AIDS transmission in sub- Saharan Africa. Bulletin of WHO, 97; 12.
- World Health Organization. (2006). Report of the HIV/Tuberculosis Fact Sheet No 104 Global and Regional Incidences.
- World Health Organization. (1994). The modes of HIV transmission fact sheet. Geneva, July 10.
- World Health Organization. (1997). HIV in Africa. Weekly Epidemiological Record, 19-21.
- Nasidi, A., Harry, T.O., Ajose-Coker, O.O., Ademilyi, S.A., Akinyanju, O. (1997). Evidence of IAV/HATIV II infections and of AIDS related complex in Lagos Nigeria. Presentation at II international conference on AIDS held in Paris.
- Mohammed, K. Chukwuedo, A.A., & Adamu, T. (2005). Prevalence of HIV/AIDS infections among pregnant women attending ante-natal clinic at specialist hospital, Sokoto. Bulletin of SAN Vol 26:294-298.
- Dimmok, N.J., & Primrose, S.B. (1995). Introduction to modern virology 4thed. Blackwell Sci Ltd, 288-305.
- Menakaya, T. (1999). HIV/syphilis, sero-prevalence survey in Nigeria. Report presented at international summit on STDs held in Abuja.
- Moderna Launches Clinical Trials for HIV Vaccine
- What is an undetectable viral load?
- Antiretrovirals: HIV and AIDS Drugs
Return from Original Research: Seroprevalence of HIV Infection among Pregnant Women Attending Antenatal Clinic in General Hospital Kumo, Gombe State Nigeria to cyprianj's Web3 Blog