Science is very interesting when you are able prove the existence of some certain things and phenomenon beyond reasonable doubt. If I recall my days in high school, a subject that was quite interesting and really worth exploring then was Geography. Really, it was fun because it had a lot of interesting stuffs one can learn. Things like formation of rain, astronomy, facts about the earth as a whole and the entire planet, earthquakes, storms, the sea tides, volcanoes, how to draw map, locations of various continents, how to calculate time zones and why time zones differ from one country to another and more.
Really, I found it interesting as a student then, even till now, they are still interesting. However, as we grow in knowledge, we have to unlearn some things to learn new ones with more facts and proves. This however does not discredit the efforts made by the scientists in bringing some of those stuffs into limelight.
Today, I have special interest in discussing something similar to volcanoes. These time, they are a special type of prokaryotic organisms that is not commonly discussed at high school level and even sometimes at the undergraduate level. These organism cause the spontaneous eruption of substance from the ground unto the surface as similarly observed in volcanoes. Sure its an interesting stuff you would want to know more about. So, get a seat, relax and enjoy!
It will be more appropriate we understand that volcanoes are formed due to the activity of tectonic plates (parts of the earth lithosphere) that moves. In the process of their movement, they may collide with each other and this can send one further below the earth surface. Remember, the higher you go on earth, the cooler in becomes, and the lower you go, the hotter it becomes. Because of this knowledge, it is believed that the tectonic plate that is sent deeper down into the earth mantle, comes in contact with hotter temperature thereby causing them to melt and form molten magma.
The molten magma later rises from the earth mantle to the crust (upper and cooler surface). Upon coming in contact with the cooler surface, the temperature drops leading to its solidification as rock. This is just a simple mechanism besides other types known. Some volcanoes could be as a result of the separation of the tectonic plates from each other thereby paving way for the molten magma (formed by the mantle) to rise up to the earth surface.
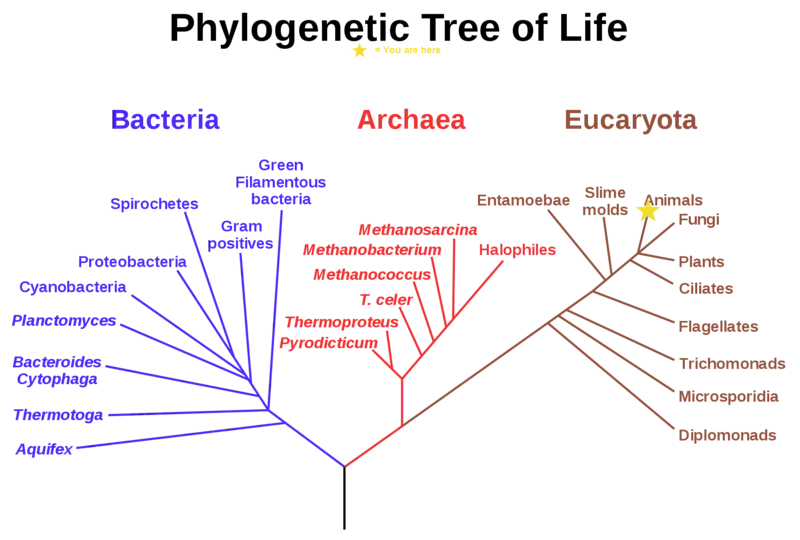
Some rocks like the igneous rock are formed through a similar as above. We won't be going into the intricacies of that. I want to tilt this article more to something similar to volcano caused by the activities of a special type of prokaryotic organisms called Archaea. Their classification stems from the tree of life which has three main branches - The Eukaryotes, prokaryotes (Bacteria) and then the Archaea.
Archaea are believed to be the closer in similarity to eukaryotes than to the prokaryotes however, they are well known to exist in places where you have no or low oxygen. In most cases, they are obligate anaerobes. The presence of oxygen is a poison to them. You find them more in water, soil and places were normal eukaryotes and bacteria would not survive.
The major characteristic feature and why they are believed to be similar in genetic content to eukaryotes is the fact that they contain ribosomal RNA and tRNA, they do not have peptidoglycan layer which is common in bacteria but have a special S-layer that makes them highly resistance to extreme salt concentration - reason why you find them in unusual habitats. In essence, regular antibiotics that ordinarily would kill bacteria if they act through the cell wall inhibition pathway, would have no effect on them.
In fact, even if you use some antibiotics that inhibit protein synthesis (e.g. tetracycline) with the exception of aminoglycosides (e.g. amikacin, neomycin, gentamycin etc.) and Fusidic acid (e.g. Fucidin), others will not work on them. The reason is simple, the ribosome in the archaea is different from those found in bacteria cells, hence they will not bind to inhibit their function.
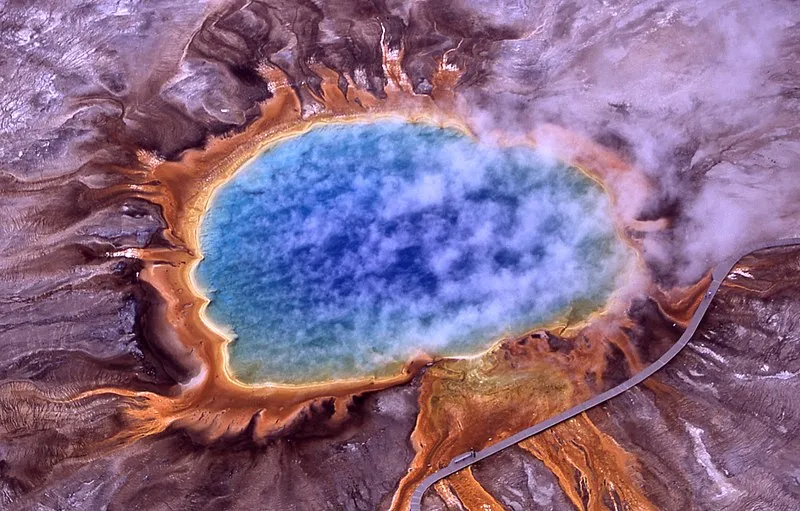
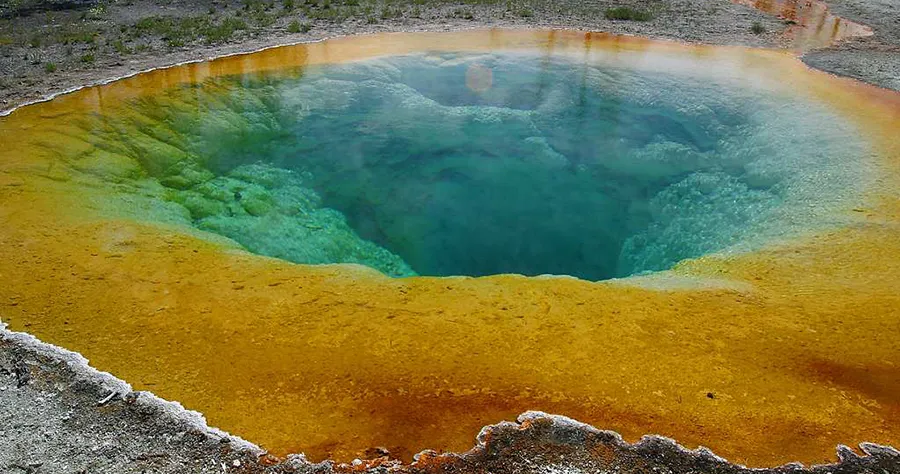 Characteristic colour of water body most possibly depicting the presence of archaea
Characteristic colour of water body most possibly depicting the presence of archaea
Generally, they are referred to as extremophiles (organism that live in extreme environments). Most times, they give beautiful characteristic colours to their environment when they are present together with other types of bacteria, so you end up seeing a very beautiful picture of water bodies (if present).
A well known example is the high salty lake in Utah, USA. The common classification of archaea includes the halophiles (those that live in environment with very high salt concentration), methanogens (those that produce methane gas as a by-product), thermophiles (those that live in very high temperature environment), acidophiles and alkalophiles just as the name suggests. There more of the classification however, our interest is not really on those.
This photo above shows steam rising from hot and sterile deep azure blue water (owing to the light absorbing overtone of an OH stretch which is shifted to 698 nm by hydrogen bonding) in the center surrounded by huge mats of brilliant orange algae, bacteria and archaea. The color of which is due to the ratio of chlorophyll to carotenoid molecules produced by the organisms. During summertime the chlorophyll content of the organisms is low and thus the mats appear orange, red, or yellow.
Among all the listed types of archaea, which one do you think produces similar phenomenon observed in volvanoes? If you guess methanogens, then for sure, you are a genius! Methanogens are the real deal and the main types of archaea that produce methane gas as a consequence of their metabolic activity. They those class that cannot tolerate the presence of oxygen around them, because they obligate anaerobes.
You find methanogens not just in soil, but also in water and the stomach of ruminant animals where they remove the products of fermentation such as Carbon dioxide and hydrogen. They are the organisms responsible for the spontaneous release of gases in vulcans.
As you know, methane is a greenhouse gas that help or play crucial role in carbon cycle. These organisms are the major source of methane aside those derived from human activities and from the guts of ruminant animals. When the methane is released into the atmosphere, it can stay there for a very long time absorbing the Ultraviolet radiation from the sun. This is one of the reason is termed as a greenhouse gas. When you compare its heat trapping capacity to that of carbon dioxide, methane takes the lead. However, it is not as abundant as carbon dioxide.
Furthermore, because of their long persistence in the atmosphere, they are prone to oxidation by hydroxyl radicals. This reaction contributes to the depletion of this gas from the atmosphere. In essence, the higher the amount of this hydroxyl radical, the faster methane is oxidized to carbon dioxide. Howbeit, the oxidation is still somewhat an important reaction because, the carbon dioxide produced can be used by plants for photosynthesis. So as you can see, it is not really a bad idea.
However, if there is an increased release of methane gas from the industrial activities of humans, it could cause global warming because, its high concentration results to higher heat trapping capability.
Methanogens have a direct impact on the climate by releasing methane, the global warming potential of which is ~30 times greater than carbon dioxide over a 100-year period. The reverse is also true. Rising global temperatures also increase the activity and abundance of methanogens in different environmental conditions. This creates a positive feedback loop, the end result of which negatively impacts all lifeforms on the planet.
Methanogens, because of their degradation ability, are mostly used in anaerobic waste treatment plants and even in water treatments. The biomethane produced as a result can even be used for energy generation. What if I told you that the flatulence in humans (the gas we release through the anus) contains methane, even when we belch (sporadic release of gas through the mouth).
Summarily, methanogens are causes of vulcans which is similar to volcanoes but the main difference is that, volcanoes are accompanied by extreme temperatures and molten magma. Vulcans produced by methanogens just contain methane gas that is released sporadically into the atmosphere. Infection with archaea can be very difficult to cure considering the fact that they are highly resistant to a wide range of broad spectrum antibiotics.
The major antibiotics that can effectively work against archaea infection are those class of antibiotics that target the genetic composition of the organism. That is, those that target the DNA. Although, not all the types of archaea are known to cause or be associated with disease in humans. Methanogens so far, are the only type known to be associated with the human gut.
Before now, archaea are reported to have no association with human disease, however, emerging facts suggests that they play role in human periodontal disease. All thanks to molecular techniques such and gene sequencing and RNA analysis. There more to what we don't know about the highly abundant organisms, time will tell!
References •The forces of nature •How volcanoes are formed •Archaebacteria •What is Archaea? •Susceptibility of archaea to antimicrobial agents: applications to clinical microbiology •The antimicrobial resistance pattern of cultured human methanogens reflects the unique phylogenetic position of archaea •How Methanogenic Archaea Contribute to Climate Change •Archaea and Their Potential Role in Human Disease •Role of archaea in human disease
Return from Volcanoes and Archaea Methanogen Vulcans: Where natural phenomenon compares to metabolic process to cyprianj's Web3 Blog